Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2016; 22(22): 5183-5192
Published online Jun 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5183
Published online Jun 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5183
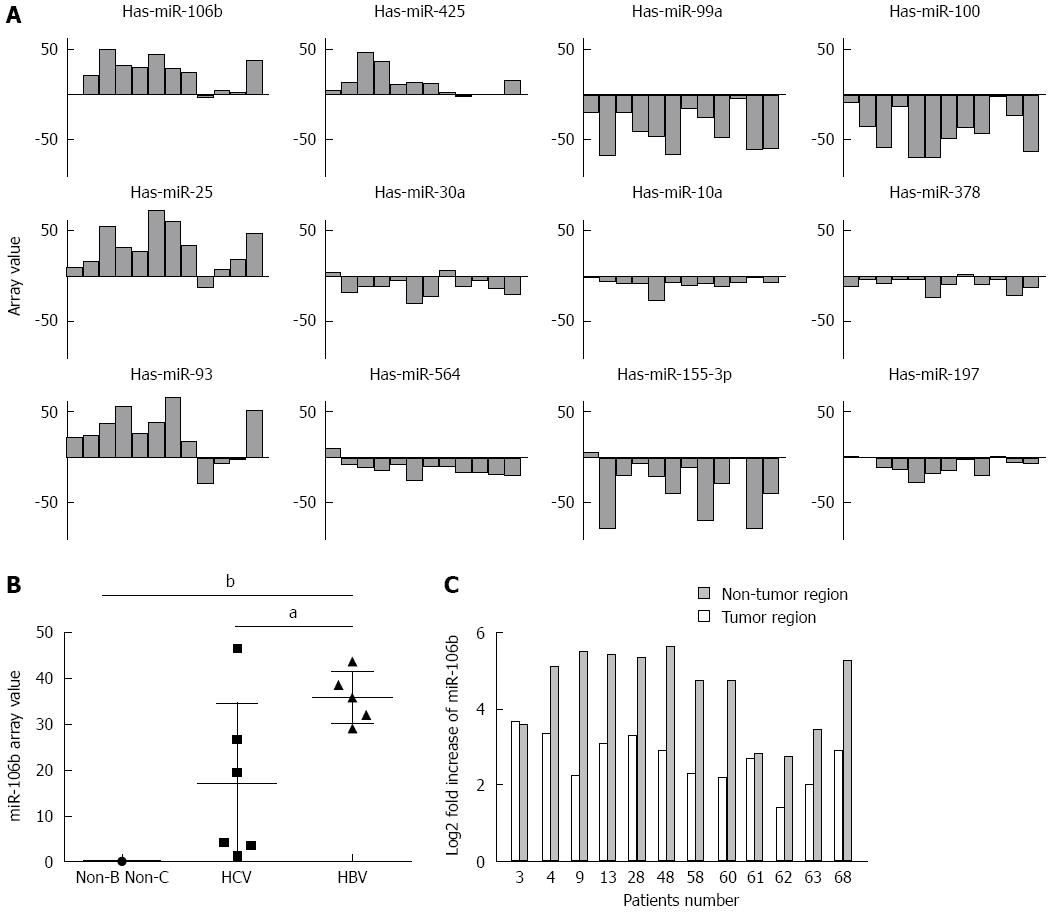
Figure 1 miRNA array analysis of the miRNA expression patterns in patients with distinct types of hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 12).
A: The top 12 miRNAs significantly dysregulated in the tumor regions of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients based on statistical results (P < 0.01); B: miR-106b expression levels in tumor regions of patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV) -associated HCC, HCV-associated HCC, and non-B/non-C HCC; C: q-RT-PCR analysis of miR-106b expression values in the tumor and adjacent non-tumor regions of patients. Fold-increases were calculated after comparing the results with the miR-106b expression levels in normal liver samples. Data represent the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001 vs HCV.
- Citation: Yen CS, Su ZR, Lee YP, Liu IT, Yen CJ. miR-106b promotes cancer progression in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(22): 5183-5192
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i22/5183.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5183