Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2016; 22(22): 5154-5164
Published online Jun 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5154
Published online Jun 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5154
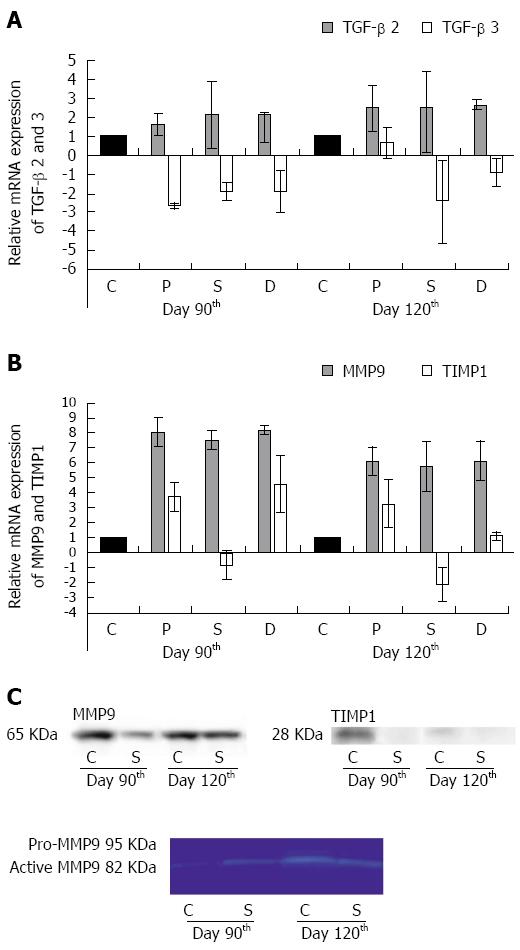
Figure 6 Relative mRNA and protein expression of transforming growth factor-beta 2 and 3, matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 in the colon of control animals and in rats treated three times with 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid.
TGF-beta 2 was up-regulated in the strictured region (S) and also in the adjacent proximal (P) and distal (D) segments of the colon as compared with the controls (C) on day 90 and day 120 (A). TGF-beta 3 gene repression was detected both 90 and 120 d after the third TNBS treatment in each colonic segment (A). The marked overexpression of MMP9 mRNA was confirmed in each colonic segment in the chronic phase of the inflammation (B). TIMP1 mRNA expression was detected in the P and D colon segments at both timepoints examined, but in the S the gene was down-regulated (B). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. 90 d after the third TNBS treatment, a decreased MMP9 protein level was detected in the S relative to the C (C, upper). Nevertheless, on day 120 the MMP9 protein expression was similar to that in the C. The activity of MMP9 was determined by gelatine zymography (C, lower). An active form of the MMP9 protein rather than pro-MMP9 was expressed in the C and S segments at both timepoints examined. Well-detectable amounts of TIMP1 protein were revealed only in the control samples from day 90 (C, right side).
- Citation: Talapka P, Berkó A, Nagy LI, Chandrakumar L, Bagyánszki M, Puskás LG, Fekete &, Bódi N. Structural and molecular features of intestinal strictures in rats with Crohn's-like disease. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(22): 5154-5164
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i22/5154.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5154