Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2016; 22(21): 5012-5022
Published online Jun 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i21.5012
Published online Jun 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i21.5012
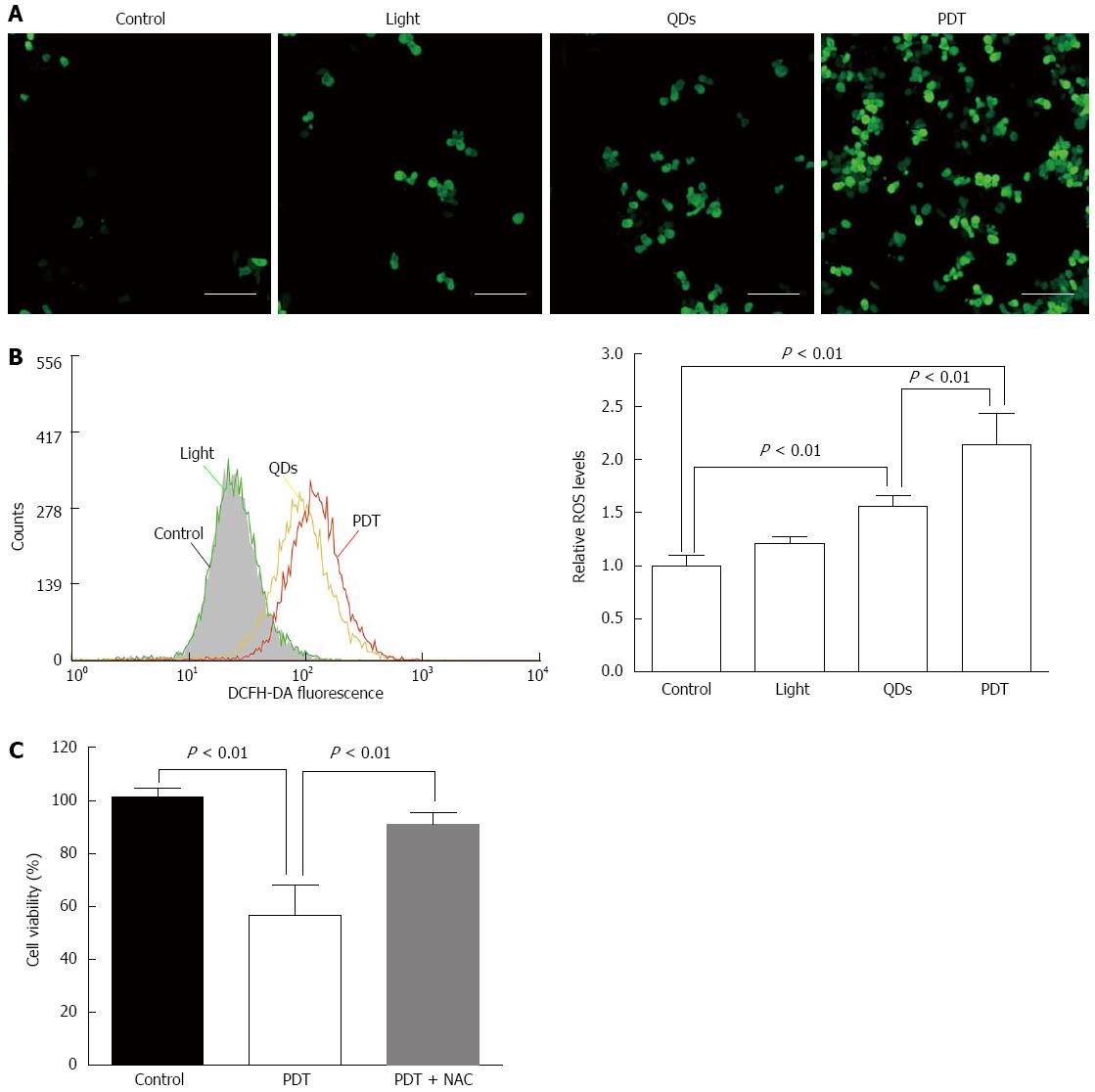
Figure 6 Reactive oxygen species generation was detected after treatment of CdSe/ZnS quantum dots with illumination.
A: Fluorescent images of ROS in SW1990 cells (Bar: 200 μm); B: Relative ROS level measured by FCM; C: Cell viability of SW1990 cells by CCK-8 assay. Control: normal SW1990 cells; Light: SW1990 cells with illumination (20 J/cm2); QDs: SW1990 cells treated with CdSe/ZnS QDs (1.5 μmol/L, 3 h); PDT: SW1990 cells treated with CdSe/ZnS QDs (1.5 μmol/L, 3 h) and illumination (20 J/cm2). NAC: N-acetylcysteine, a ROS scavenger, 5 mmol/L NAC was added to the cell culture for 1 h before treatment. QDs: Quantum dots; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: He SJ, Cao J, Li YS, Yang JC, Zhou M, Qu CY, Zhang Y, Shen F, Chen Y, Li MM, Xu LM. CdSe/ZnS quantum dots induce photodynamic effects and cytotoxicity in pancreatic cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(21): 5012-5022
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i21/5012.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i21.5012