Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2016; 22(20): 4891-4900
Published online May 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i20.4891
Published online May 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i20.4891
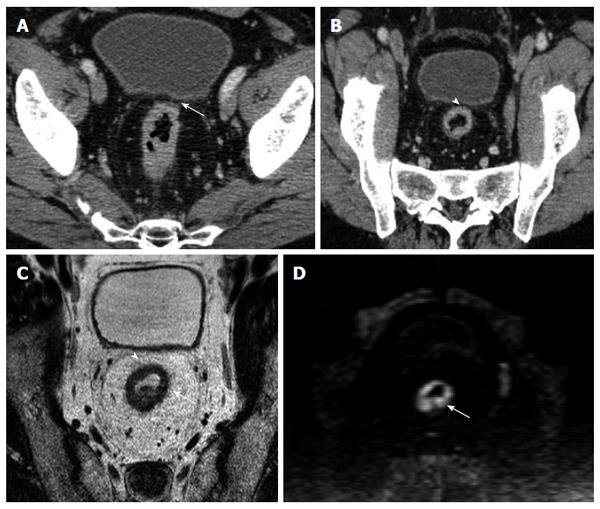
Figure 4 Images obtained in a 68 years-old man with high rectal cancer.
A: Axial computed tomography (CT) image shows a tumor as a circumferential thickening in the bowel wall; in the anterior wall (arrow) the tumor seems to involve the mesorectal fascia (MRF); B: Multiplanar reconstruction CT images shows a visible fat line between the tumor and the MRF (arrowhead); C: Axial T2-weighted magnetic resonance image shows a rectal wall involvement by the tumor but also a wide fat pad between the tumor and the free MRF; D: DWIBS image (b-value 1000), the tumor is depicted as a high signal circumferential thickening of the bowel wall, in comparison with the lower signal intensity of surrounding tissue.
- Citation: Ippolito D, Drago SG, Franzesi CT, Fior D, Sironi S. Rectal cancer staging: Multidetector-row computed tomography diagnostic accuracy in assessment of mesorectal fascia invasion. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(20): 4891-4900
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i20/4891.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i20.4891