Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2016; 22(19): 4673-4684
Published online May 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i19.4673
Published online May 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i19.4673
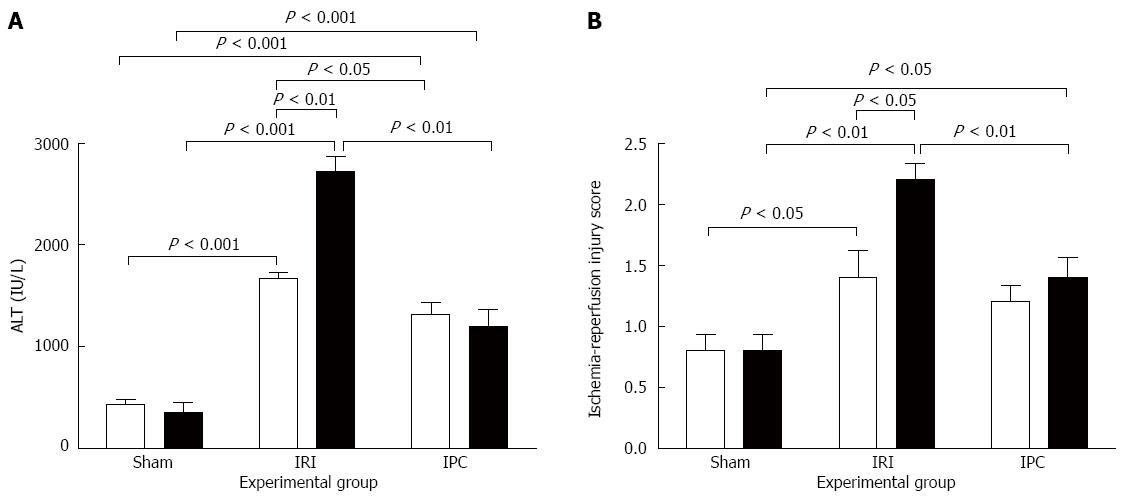
Figure 2 Serum alanine aminotransferase levels and histology injury score following ischemia-reperfusion.
Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (A) and histology injury score (B) following reperfusion were significantly higher in rats subjected to IRI compared to sham rats. Both injury markers were significantly higher in obese rats compared to lean rats. Compared to corresponding IRI groups, IPC decreased ALT levels in both lean and obese rats and decreased injury score in obese rats. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 10 rat/group; lean rats, open bar; obese rats, closed bar). IRI: Ischemia-reperfusion injury; IPC: Ischemic preconditioning.
- Citation: Chu MJ, Premkumar R, Hickey AJ, Jiang Y, Delahunt B, Phillips AR, Bartlett AS. Steatotic livers are susceptible to normothermic ischemia-reperfusion injury from mitochondrial Complex-I dysfunction. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(19): 4673-4684
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i19/4673.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i19.4673