Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2016; 22(18): 4529-4537
Published online May 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i18.4529
Published online May 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i18.4529
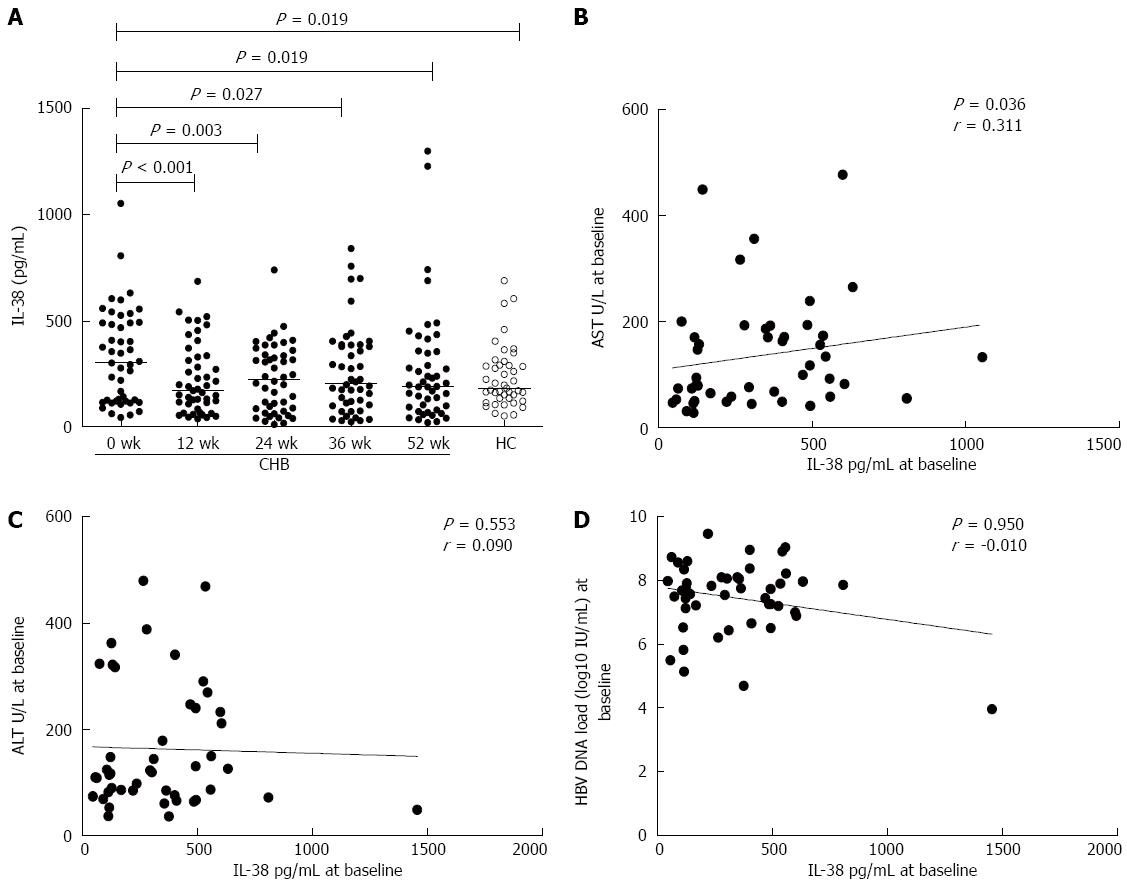
Figure 1 Kinetic changes in serum interleukin-38 levels of patients with chronic hepatitis B during treatment with telbivudine and association of serum interleukin-38 with serum aspartate transferase, alanine transferase, hepatitis B virus DNA loads prior to treatment.
A: Kinetic changes in the levels of serum IL-38 in HCs and patients with CHB at baseline and at 12, 24, 36, and 52 wk of LdT treatment. IL-38 levels were higher in patients with CHB compared with HCs at baseline [306.97 (123.26-492.79) pg/mL vs 184.50 (135.56-292.16) pg/mL; P = 0.019]. They were reduced at week 12, 24, 36, and 52 of LdT treatment (P < 0.001, P = 0.003, P = 0.027, P = 0.019), and the levels of serum IL-38 in patients with CHB were no longer different from that of the HCs after 12 wk of LdT treatment. B: Serum AST levels correlated with serum IL-38 levels at baseline. C and D: Serum IL-38 levels did not correlate with serum ALT levels or with serum HBV DNA loads at baseline. IL-38: Interleukin-38; HCs: Healthy controls; CHB: Chronic hepatitis B; LdT: Telbivudine; ALT: Alanine transferase; AST: Aspartate transferase; HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
- Citation: Wang HJ, Jiang YF, Wang XR, Zhang ML, Gao PJ. Elevated serum interleukin-38 level at baseline predicts virological response in telbivudine-treated patients with chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(18): 4529-4537
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i18/4529.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i18.4529