Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2016; 22(18): 4501-4514
Published online May 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i18.4501
Published online May 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i18.4501
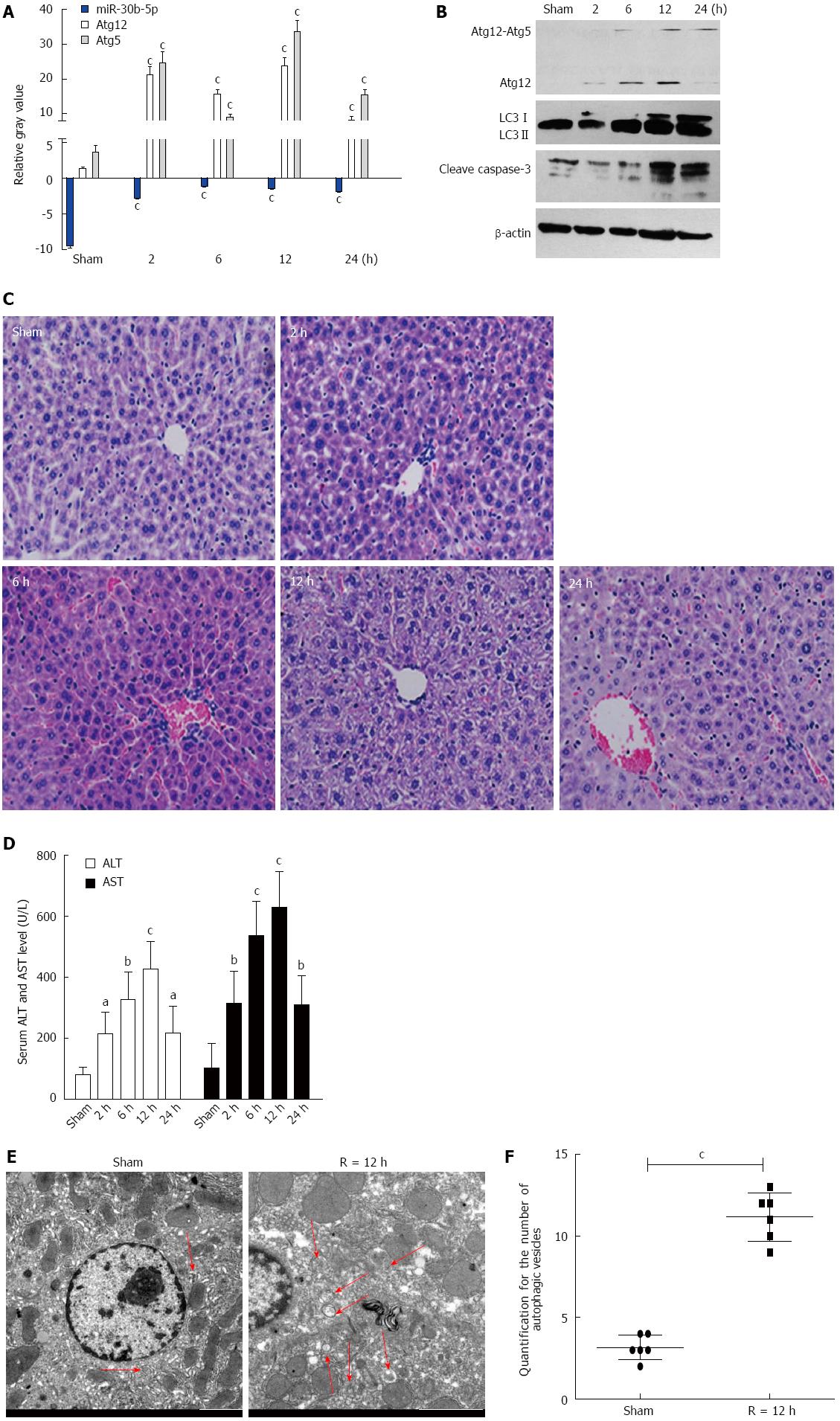
Figure 1 Alterations of miR-30b and autophagy in mouse livers in response to ischemia-reperfusion injury.
A: The expression of miR-30b in mouse livers subjected to IR as determined by quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction analysis; B: Western blotting for autophagy-related gene (Atg) 12, light chain 3 (LC3), and cleave caspase-3 in mouse liver; C: IR treatment increases the histopathologic changes in liver (magnification × 200); D: IR treatment increased serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels in mice compared with sham; E: Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of mouse hepatocytes after ischemia followed by reperfusion at 12 h. Scale bars = 2.0 μm. The data were quantified by counting the number of autophagosomes per cross-sectioned cell. aP < 0.05,bP < 0.01,cP < 0.001 vs Sham group. Every experiment was repeated three times.
- Citation: Li SP, He JD, Wang Z, Yu Y, Fu SY, Zhang HM, Zhang JJ, Shen ZY. miR-30b inhibits autophagy to alleviate hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury via decreasing the Atg12-Atg5 conjugate. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(18): 4501-4514
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i18/4501.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i18.4501