Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2016; 22(18): 4466-4483
Published online May 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i18.4466
Published online May 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i18.4466
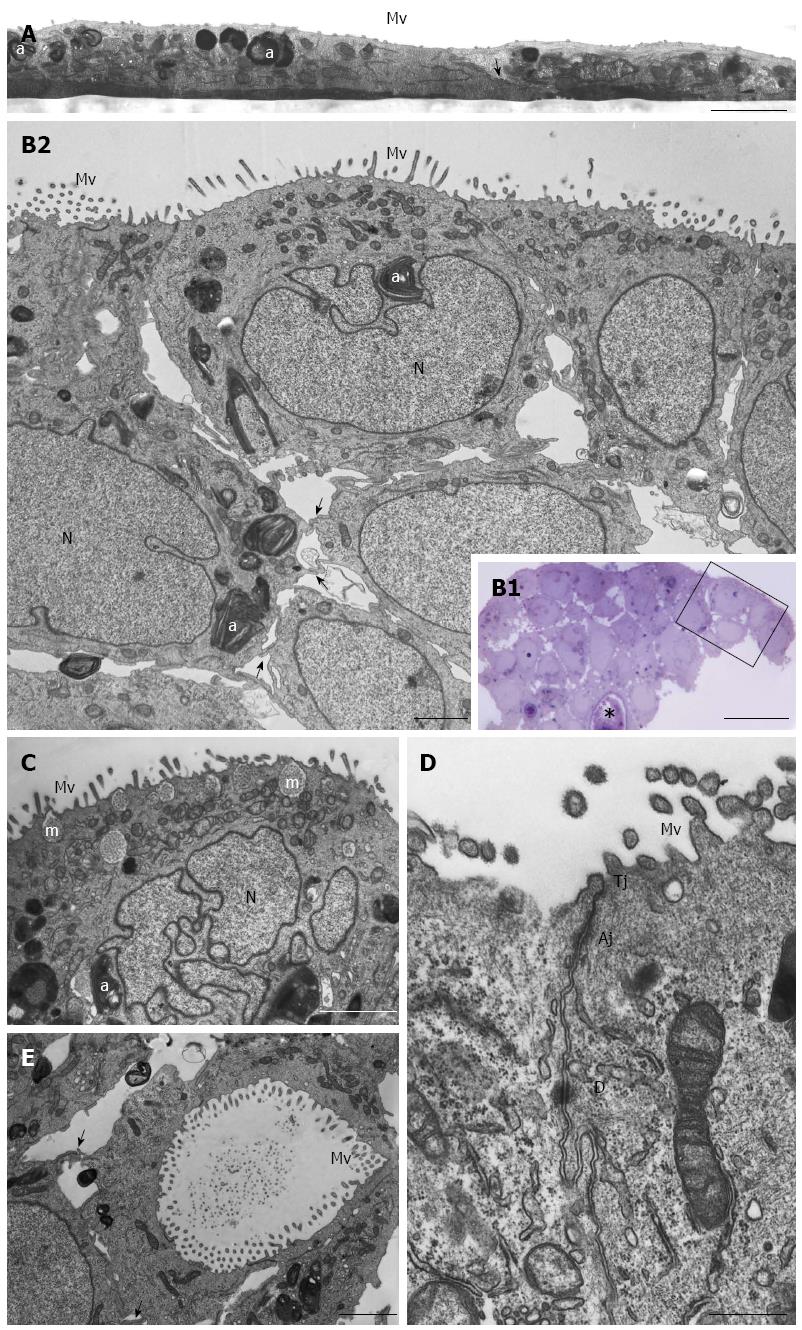
Figure 3 HPAC ultrastructure.
A: Electron microscopy of a HPAC 2D-monolayer. Two cells having dark and light cytoplasm, respectively, are partially overlapped and interdigitated by finger-like projections (arrow); sparse and short microvilli (Mv) in the domain facing the culture medium and some autophagosomes (a) can be seen. Scale bar = 2 μm; B1: Light microscopy of a semi-thin section showing a representative area of a multilayered 3D-spheroid. The asterisk indicates a lumen-like structure. Ultrastructural features of the boxed area are shown in B2. Scale bar = 20 μm; B2: Electron microscopy of the thin section immediately adjacent to the semi-thin one, and corresponding to the boxed area in B1, shows cellular polarity and numerous microvilli (Mv) in the apical domain facing the culture medium. Several autophagosomes (a) can be observed in the cytoplasm. Cells of the lower region exhibit interdigitating finger-like processes (arrows) in the interstitial space. Nuclei (N) are euchromatic and frequently display more or less deep invaginations. Scale bar = 5 μm; C: Micrograph showing a cell with a markedly irregular nucleus (N) and several mucin granules (m) in the apical cytoplasm. Scale bar = 2 μm; D: Thin section of two adjacent cells located at the periphery of the spheroid and facing the culture medium. Microvilli (Mv) in the apical domain and a junctional complex, consisting of tight junction (Tj), adherens junction (Aj), and desmosome (D) in the lateral domain, can be observed. Scale bar = 0.5 μm; E: Micrograph of the inner part of a spheroid in which some adjacent interdigitated cells (arrows) delimiting a lumen-like structure exhibit numerous microvilli in their apical domains and junctional specializations (arrows). Scale bar = 2 μm
- Citation: Gagliano N, Celesti G, Tacchini L, Pluchino S, Sforza C, Rasile M, Valerio V, Laghi L, Conte V, Procacci P. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Characterization in a 3D-cell culture model. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(18): 4466-4483
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i18/4466.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i18.4466