Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2016; 22(15): 3969-3977
Published online Apr 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i15.3969
Published online Apr 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i15.3969
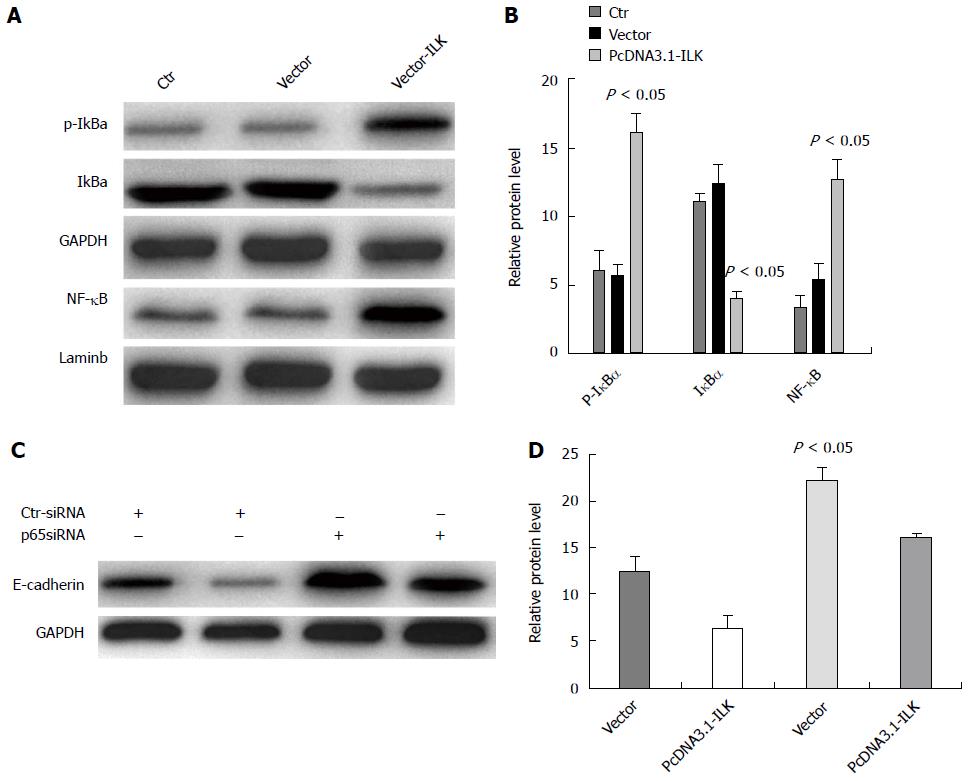
Figure 8 Nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway mediated the integrin-linked kinase-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition occurrence.
A: Western blot detection of p-IκBa, IγBa, and NF-κB expression; B: Statistical analysis, in which the difference between the vector group and vector-ILK group was statistically significant; C: After treatment with siRNA, E-cadherin expression was detected in cells; D: Statistical analysis: the difference between the vector-ILK cell line in the siRNAp65 treated group and control siRNA group was statistically significant. This experiment was repeated three times. ILK: Integrin-linked kinase; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; siRNA, small interfering RNA.
- Citation: Shen H, Ma JL, Zhang Y, Deng GL, Qu YL, Wu XL, He JX, Zhang S, Zeng S. Integrin-linked kinase overexpression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via nuclear factor-κB signaling in colorectal cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(15): 3969-3977
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i15/3969.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i15.3969