Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2016; 22(14): 3869-3874
Published online Apr 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3869
Published online Apr 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3869
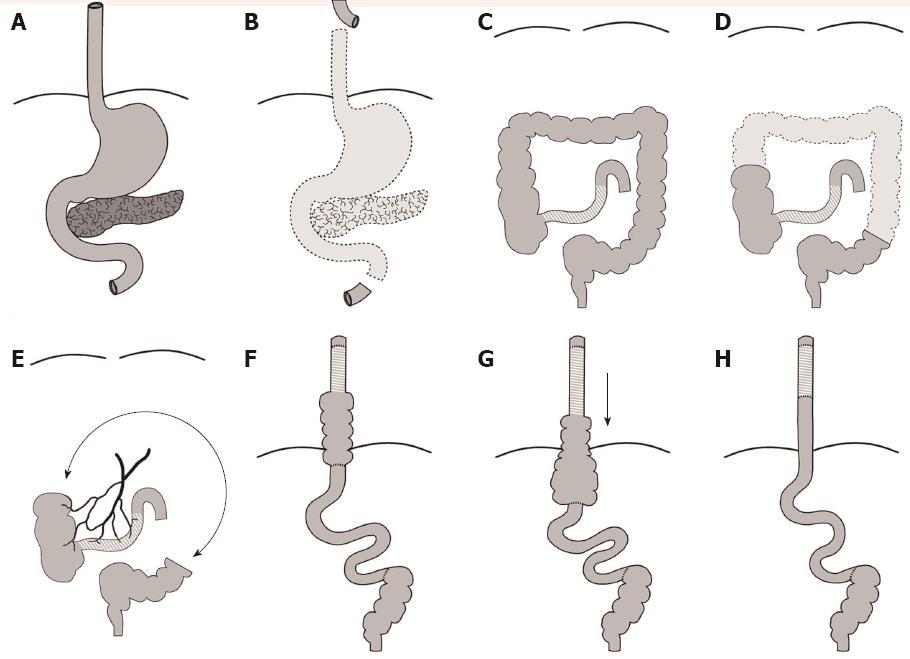
Figure 1 Secondary reconstruction with an ileo-right hemi-colonic cervical pull-up on a non-supercharged ileocolic arterial pedicle.
A, B: Before and after emergency esophagectomy, gastrectomy, duodenectomy and pancreatectomy due to a caustic injury with hydrochloric acid; C, D: Esophageal reconstruction with transverse and descending colon fails due to ischemic demarcation → consecutive resection of transverse and descending colon including the distal part of the ascending colon; E: A short stump of the right hemi-colon and approximately 40 cm of descending colon were left in situ, connected via a colo-colonic anastomosis; F: Esophageal reconstruction with an ileo-right hemi-colonic cervical pull-up on a non-supercharged ileocolic arterial pedicle in an isoperistaltic direction; G: Situation 9 mo after reconstruction: The cecal part of the pulled-up graft had moved downwards from the thoracic cavity into the abdomen and largely dilated, causing recurrent episodes of bowel obstruction; H: Final result: The ileocecal region was resected and an ileo-jejunostomy was formed.
- Citation: Weiss AR, Hackl C, Soeder Y, Schlitt HJ, Dahlke MH. Ileo-right hemi-colonic cervical pull-up on a non-supercharged ileocolic arterial pedicle: A technical and case report. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(14): 3869-3874
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i14/3869.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3869