Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2016; 22(14): 3746-3757
Published online Apr 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3746
Published online Apr 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3746
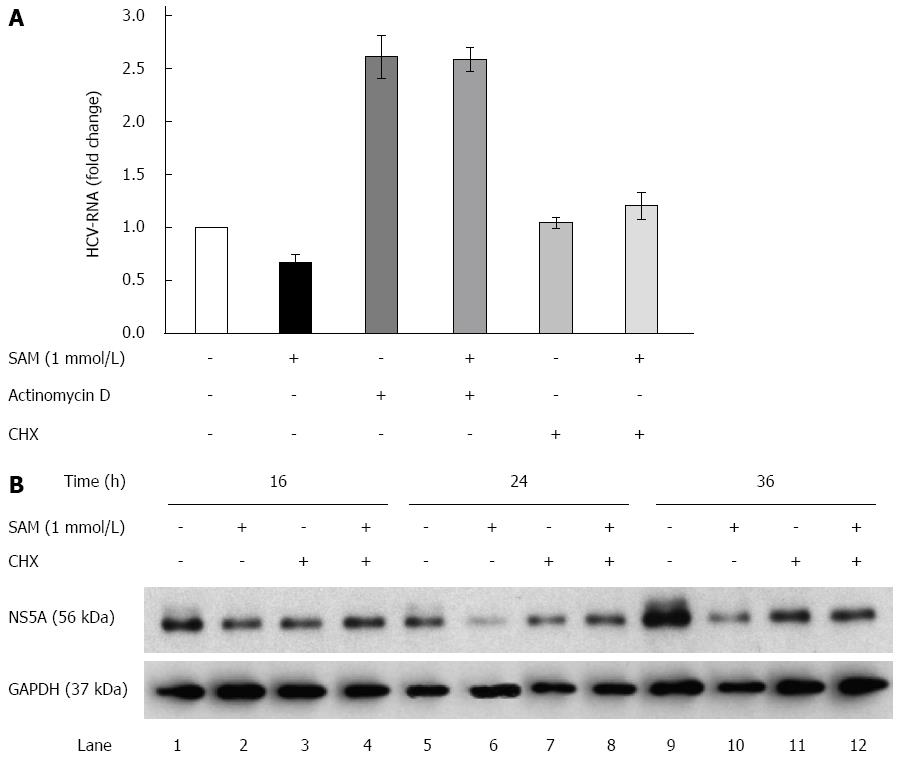
Figure 3 Role of actinomycin D and cycloheximide on the antiviral effect of S-adenosyl-L-methionine.
A: SAM decreases replicon RNA levels without affecting its stability. Huh7 HCV replicon cells (1.5 × 105 cells) were incubated with SAM 1 mmol/L, some cells were treated with actinomycin D (4 μg/mL) or CHX (50 μg/mL) for 2 h, then SAM was added. Cells were harvested 16 h later and HCV-RNA levels were quantified by real-time RT-PCR and normalized with GAPDH using ΔΔCt method. Mean results from three experiments are shown; B: CHX partially reverts the downregulated NS5A protein expression induced by SAM. Huh7 HCV replicon cells (1.5 × 105 cells) were incubated with SAM 1 mmol/L, some cells were treated CHX (50 μg/mL) after 4 h of SAM treatment. Cells were harvested at different time points (0-36 h), then total protein was extracted and western blot for NS5A and GAPDH was performed. CHX: Cycloheximide; SAM: S-adenosyl-L-methionine; HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
- Citation: Lozano-Sepulveda SA, Bautista-Osorio E, Merino-Mascorro JA, Varela-Rey M, Muñoz-Espinosa LE, Cordero-Perez P, Martinez-Chantar ML, Rivas-Estilla AM. S-adenosyl-L-methionine modifies antioxidant-enzymes, glutathione-biosynthesis and methionine adenosyltransferases-1/2 in hepatitis C virus-expressing cells. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(14): 3746-3757
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i14/3746.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3746