Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2016; 22(13): 3592-3601
Published online Apr 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i13.3592
Published online Apr 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i13.3592
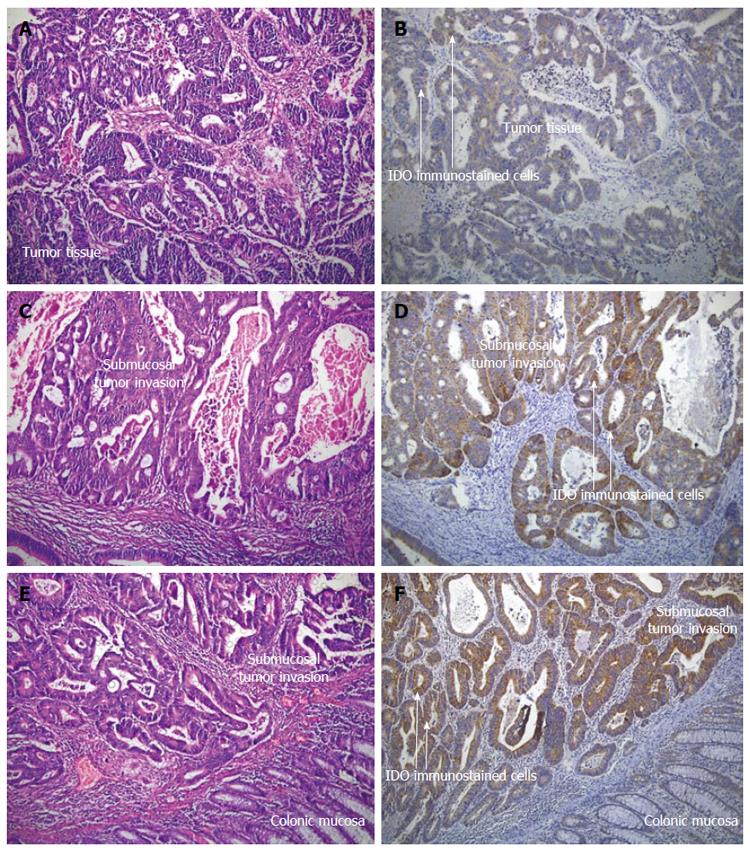
Figure 1 Hematoxylin and eosin stained (A, C and E) and indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase immunostained (B, D and F) materials for the histopathological evaluation of colorectal carcinoma patients (Magnification × 100).
The presence of lymphatic invasion, indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) intensity, IDO proportion and total IDO immunostaining scores were determined by antibodies against IDO (Tumor cells show strong positive staining while normal mucosa shows negative or very weak staining). A and B: Lymphatic invasion negative, IDO intensity, 3: IDO proportion score, 5%: total IDO immunostaining score, 4; C and D: Lymphatic invasion positive, IDO intensity, 3: IDO proportion score, 70%: total IDO immunostaining score, 6; E and F: Lymphatic invasion positive, IDO intensity, 3: IDO proportion score, 90%: total IDO immunostaining score, 7.
- Citation: Engin A, Gonul II, Engin AB, Karamercan A, Sepici Dincel A, Dursun A. Relationship between indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity and lymphatic invasion propensity of colorectal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(13): 3592-3601
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i13/3592.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i13.3592