Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2016; 22(13): 3531-3546
Published online Apr 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i13.3531
Published online Apr 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i13.3531
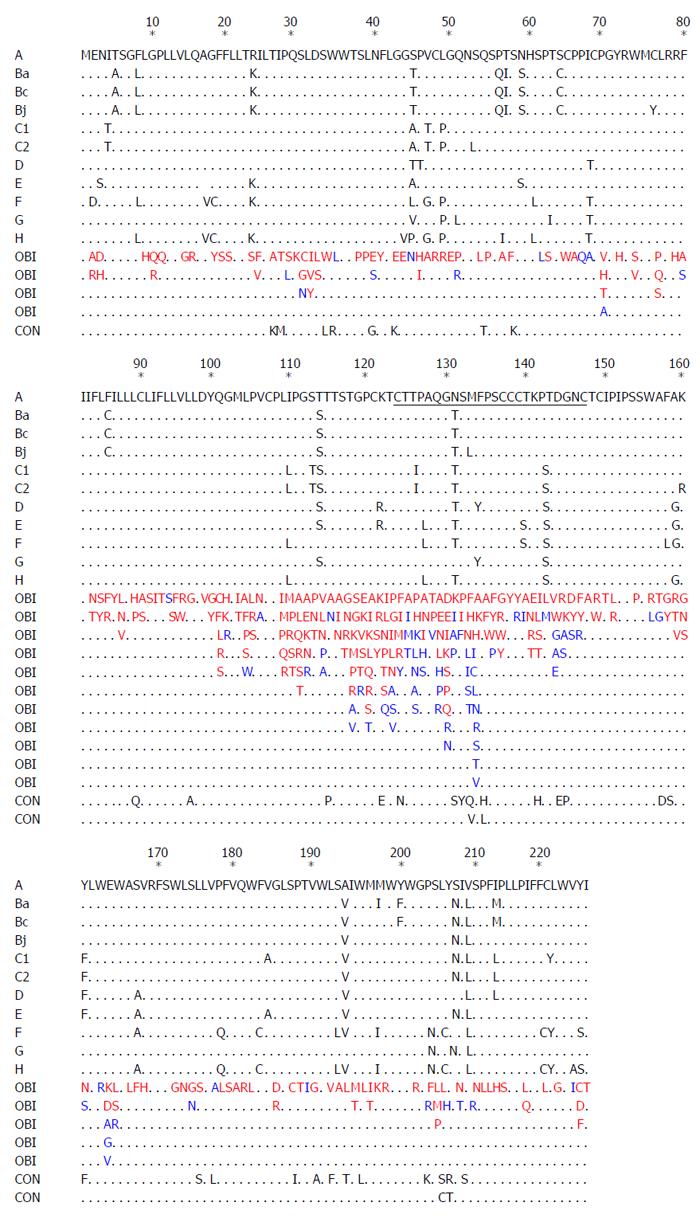
Figure 1 Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the 226AA hepatitis B virus, hepatitis B virus surface antigen between occult hepatitis B virus infections, and controls.
Amino acid substitutions are indicated with one-letter codes. Mutations identified in occult hepatitis B virus infections group and control group are in red and black, respectively. Mutations detected in both groups are in blue. Black dots denote amino acid identity with any of the reference strains of genotype A to H retrieved from GenBank (accession numbers: A, X02763; Ba, D00330; Bc, GQ205440; Bj, AB073858; C1, KM999990; C2, KM999991; D, X02496; E, X75657; F, X69798; G, AF160501; H, AY090454). Genotype-specific substitutions are listed. CON indicates control.
- Citation: Zhu HL, Li X, Li J, Zhang ZH. Genetic variation of occult hepatitis B virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(13): 3531-3546
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i13/3531.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i13.3531