Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2016; 22(10): 2971-2980
Published online Mar 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i10.2971
Published online Mar 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i10.2971
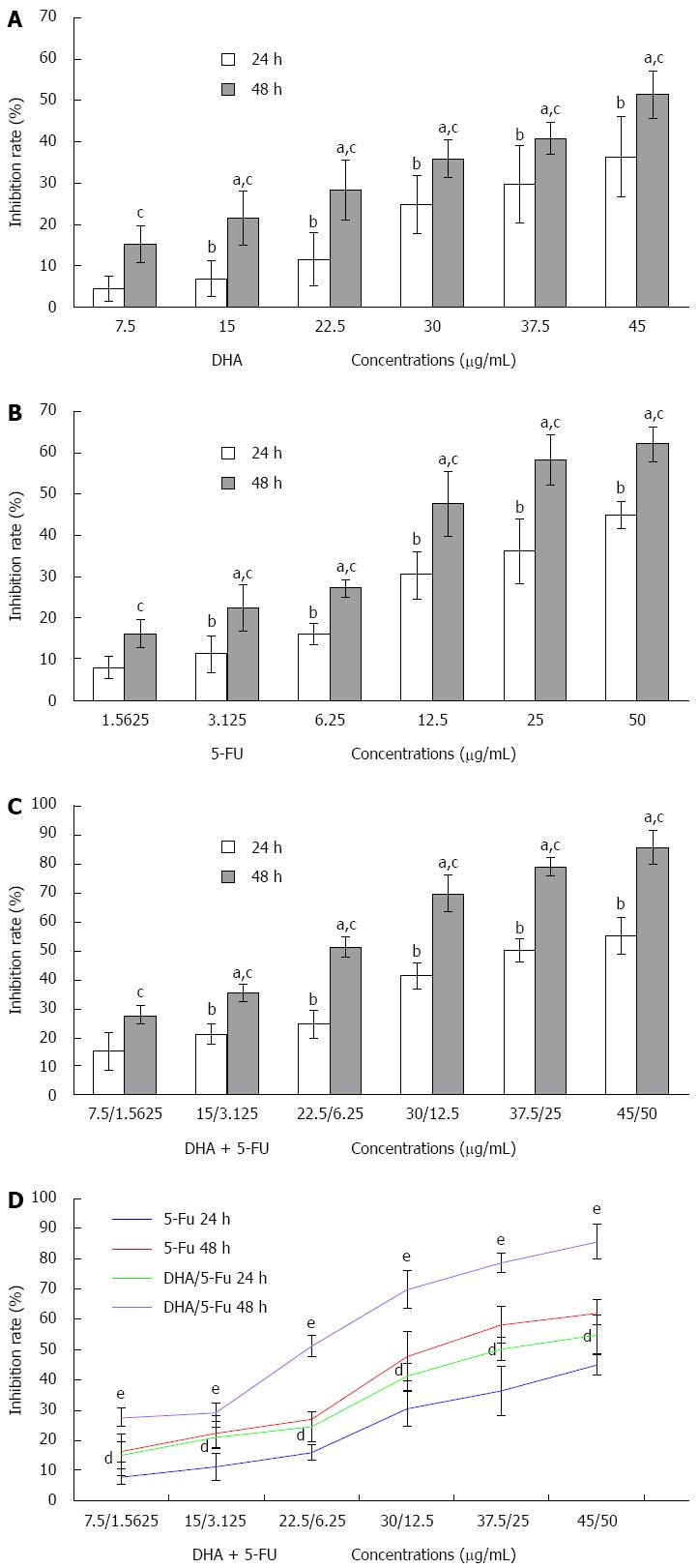
Figure 1 Inhibitory effect of docosahexaenoic acid or/and 5-fluorouracil on the growth of AGS cells.
A-C: Growth inhibition rate of AGS following 24 or 48 h treatment with increasing concentrations of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) alone or in combination. The inhibition was in a significant time and dose-dependent manner; D: DHA notably increased 5-FU cytotoxicity. aP < 0.05 vs cells treated with DHA (7.50 μg/mL), 5-FU (1.5625 μg/mL), and DHA (7.5 μg/mL) plus 5-FU (1.5625 μg/mL) for 48 h, respectively; bP < 0.05 vs cells treated with DHA (7.50 μg/mL), 5-FU (1.5625 μg/mL), and DHA (7.50 μg/mL) plus 5-FU (1.5625 μg/mL) for 24 h, respectively; cP < 0.05 vs cells treated with various concentrations of DHA, 5-FU and DHA plus 5-FU for 24 h, respectively; dP < 0.05 vs cells treated with a series of concentrations of 5-FU alone for 24 h; eP < 0.05 vs cells treated with a series of concentrations of 5-FU alone for 48 h.
- Citation: Gao K, Liang Q, Zhao ZH, Li YF, Wang SF. Synergistic anticancer properties of docosahexaenoic acid and 5-fluorouracil through interference with energy metabolism and cell cycle arrest in human gastric cancer cell line AGS cells. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(10): 2971-2980
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i10/2971.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i10.2971