Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2016; 22(10): 2931-2948
Published online Mar 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i10.2931
Published online Mar 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i10.2931
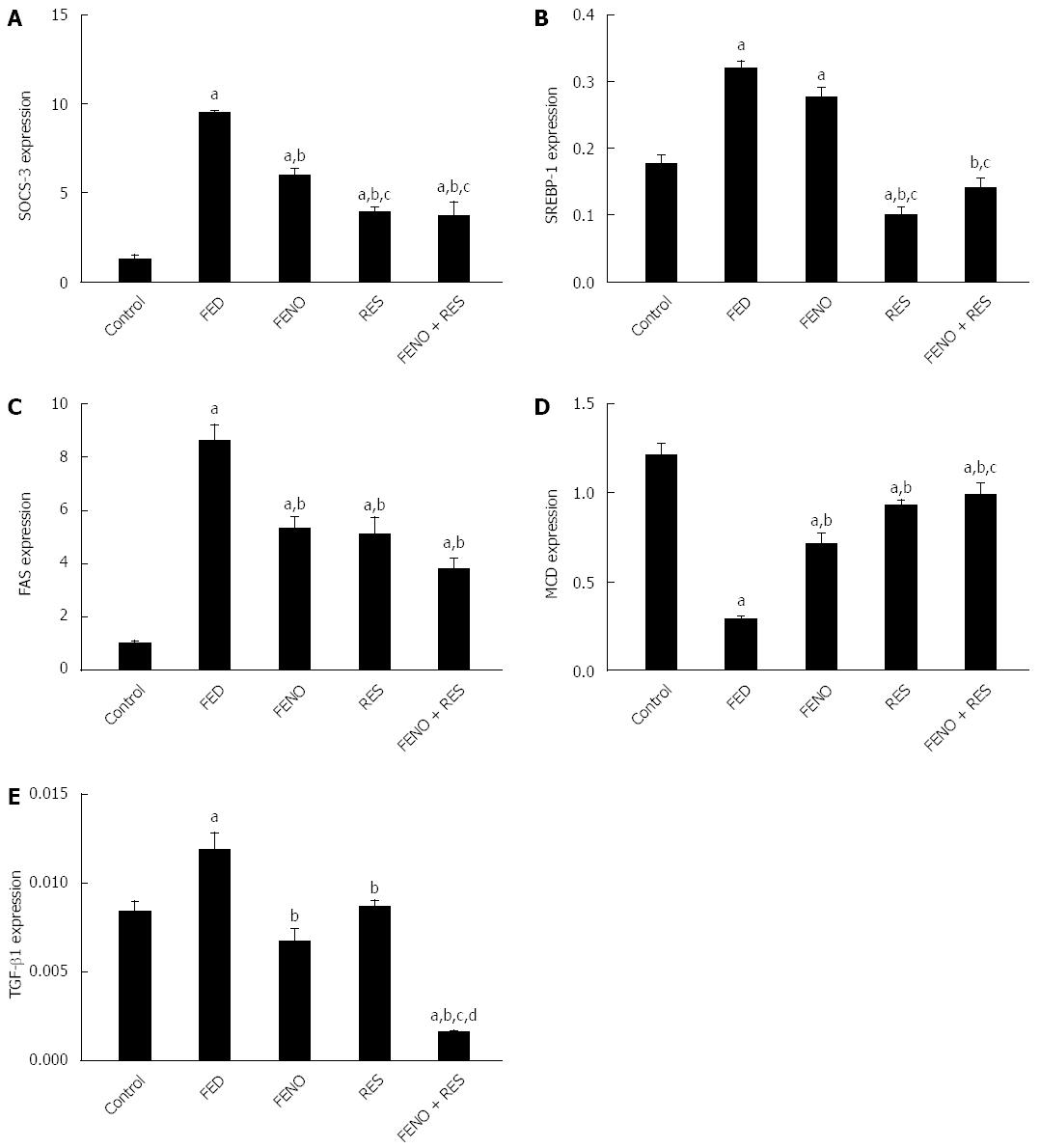
Figure 6 Effect of fenofibrate (100 mg/kg) and resveratrol (70 mg/kg) alone and in combination (half doses) on hepatic genes expression: SOCS-3 (A), SREBP-1c (B), FAS (C), MCD (D) and TGF-β1 (E) in fructose-induced NASH in rats.
Gene expression (level of mRNA) was expressed in arbitrary units based on calculation expression level relative to the internal standard. Values are mean ± SE, n = 8-12 rats.The significance of the difference between means was tested by ANOVA followed by Tukey Kramer multiple comparisons test. aP < 0.05 vs control; bP < 0.05 vs FED; cP < 0.05 vs FENO; dP < 0.05 vs RES. FED: Fructose enriched diet; FENO: Fenofibrate; RES: Resveratrol; SOCS-3: Suppressor of cytokine signalling-3; SREBP-1c: Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; MCD: Malonyl Co-A decarboxylase.
- Citation: Abd El-Haleim EA, Bahgat AK, Saleh S. Resveratrol and fenofibrate ameliorate fructose-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by modulation of genes expression. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(10): 2931-2948
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i10/2931.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i10.2931