Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2015; 21(9): 2700-2710
Published online Mar 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2700
Published online Mar 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2700
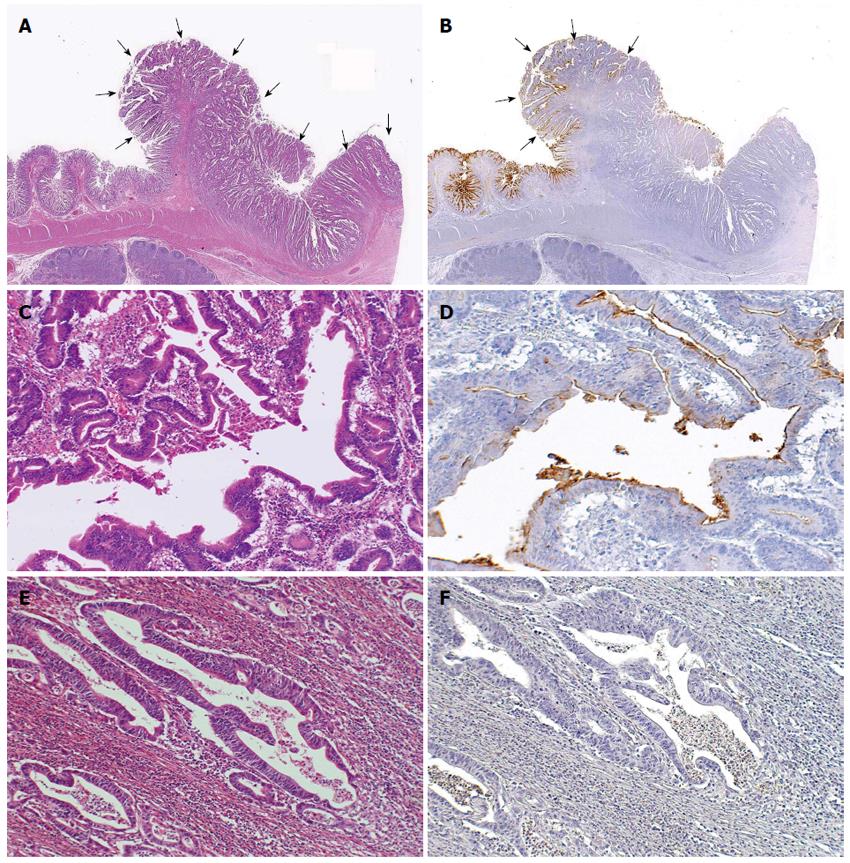
Figure 1 Representative CD10-positive small intestinal adenocarcinoma case.
A: Well differentiated adenocarcinoma (pointed by arrows) (HE stain, × 12.5); B: CD10-positive glands were seen in the superficial area and the edge of the adenocarcinoma (left, pointed by arrows), while CD10-negative glands were seen in the center or deep area of the tumor (right) (CD10, × 12.5); C, D: These glands in the surface area were positive for CD10 (HE stain and CD10, × 200); E, F: Other glands in the deeper invasive area were negative for CD10 and showed more evident loss of nuclear polarity compared to the CD10-positive glands (HE stain and CD10, × 200).
- Citation: Kumagai R, Kohashi K, Takahashi S, Yamamoto H, Hirahashi M, Taguchi K, Nishiyama K, Oda Y. Mucinous phenotype and CD10 expression of primary adenocarcinoma of the small intestine. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(9): 2700-2710
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i9/2700.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i9.2700