Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2015; 21(7): 2067-2072
Published online Feb 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i7.2067
Published online Feb 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i7.2067
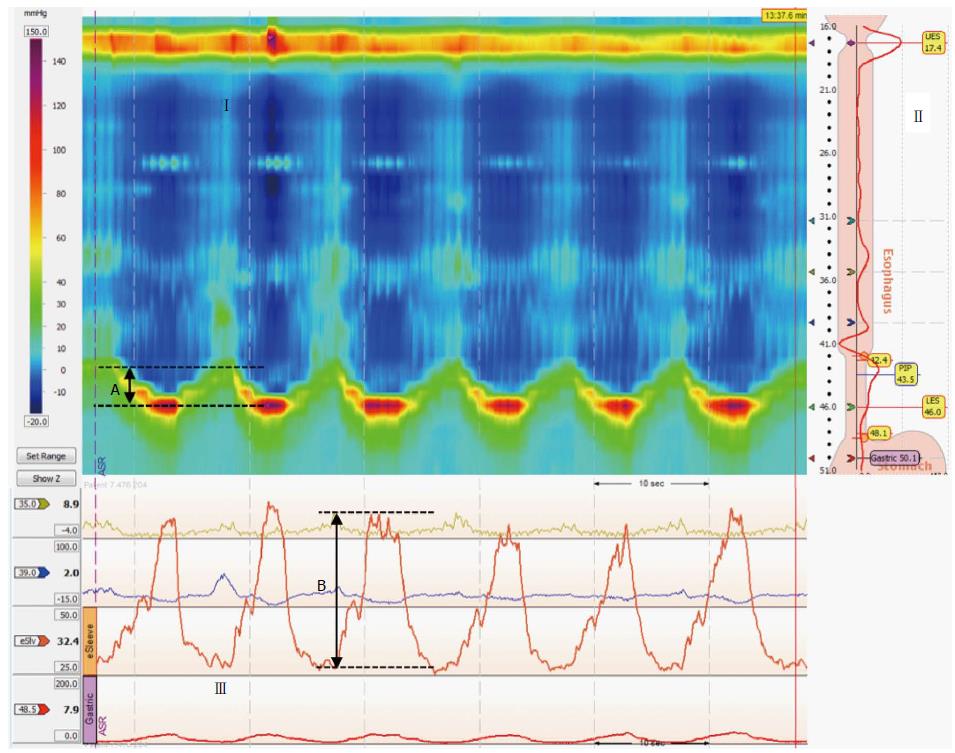
Figure 1 Sinus arrhythmia maneuver.
(Upper panels) Esophageal and esophagogastric junction (EGJ) pressure topography is shown during six 5-s inhalations (I). Inspiratory diaphragm lowering was then determined (A). The analysis landmarks are presented in the upper right panel (II). In this case, the e-sleeve extended approximately 6 cm across the EGJ. (Lower panel) (III) Esophageal and EGJ pressure tracings during sinus arrhythmia maneuver (SAM) where inspiratory peak pressures were measured (B) relative to expiratory pressure.
- Citation: Nobre e Souza MÂ, Bezerra PC, Nobre RA, Holanda ESDF, Santos AAD. Increased inspiratory esophagogastric junction pressure in systemic sclerosis: An add-on to antireflux barrier. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(7): 2067-2072
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i7/2067.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i7.2067