Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2015; 21(5): 1531-1545
Published online Feb 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1531
Published online Feb 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1531
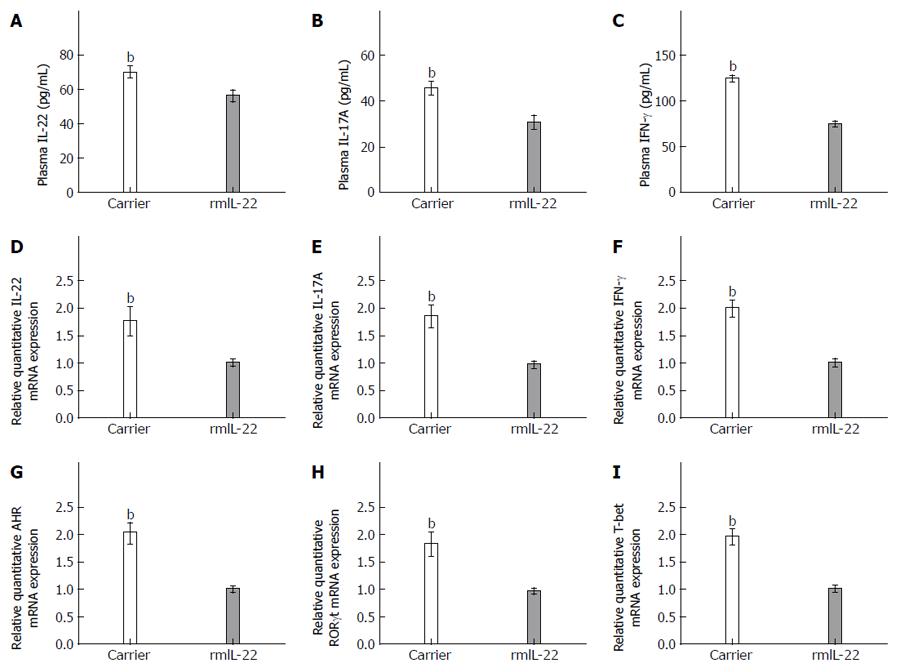
Figure 7 Expression of T helper 22-, T helper 17- and T helper 1-related cytokines was decreased in the recombinant interleukin-22 group.
A-C: The levels of plasma interleukin (IL)-22, IL-17A and interferon (IFN)-γ, measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, in the recombinant IL (rmIL)-22 group and the carrier group; D-I: The mRNA levels of liver IL-22, IL-17A, IFN-γ, aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), retinoid-related orphan receptor γ (RORγt) and T-bet in the rmIL-22 group and the carrier group. bP < 0.01 vs the carrier group. Data are mean ± SD (n = 8).
- Citation: Lu DH, Guo XY, Qin SY, Luo W, Huang XL, Chen M, Wang JX, Ma SJ, Yang XW, Jiang HX. Interleukin-22 ameliorates liver fibrogenesis by attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation and downregulating the levels of inflammatory cytokines. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(5): 1531-1545
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i5/1531.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1531