Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2015; 21(5): 1518-1530
Published online Feb 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1518
Published online Feb 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1518
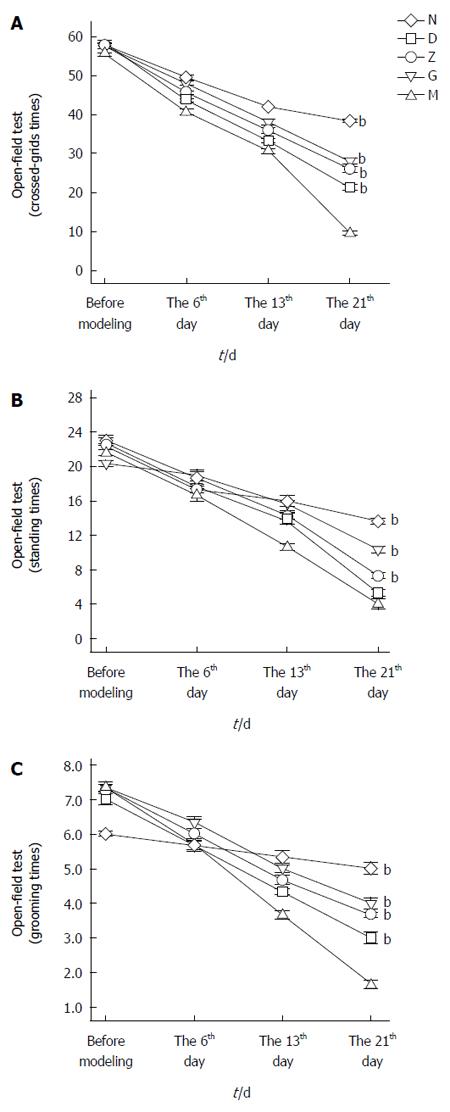
Figure 2 Open-field test of the five groups of rats.
A: Number of grids crossed: (instances that three or more paws crossed into adjacent grids); B: Standing number (number of times two forelimbs were lifted up from the bottom of box to make the body upright); C: Grooming times (number of times two forelimbs were used for grooming, scratching, or licking face and paws). Data are presented as mean ± SE. N: Primary control group; M: Depression model group; D: Low dose Xiaoyaosan (XYS) group; Z: Middle dose XYS group; G: High dose XYS group. On the 21st day, the difference between the depression model group and the primary control group was significant (n = 9; bP < 0.01 vs M). The difference between the XYS groups and the depression model group was significant (n = 9; bP < 0.01 vs M).
- Citation: Li P, Tang XD, Cai ZX, Qiu JJ, Lin XL, Zhu T, Owusu L, Guo HS. CNP signal pathway up-regulated in rectum of depressed rats and the interventional effect of Xiaoyaosan. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(5): 1518-1530
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i5/1518.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1518