Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2015; 21(5): 1498-1509
Published online Feb 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1498
Published online Feb 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1498
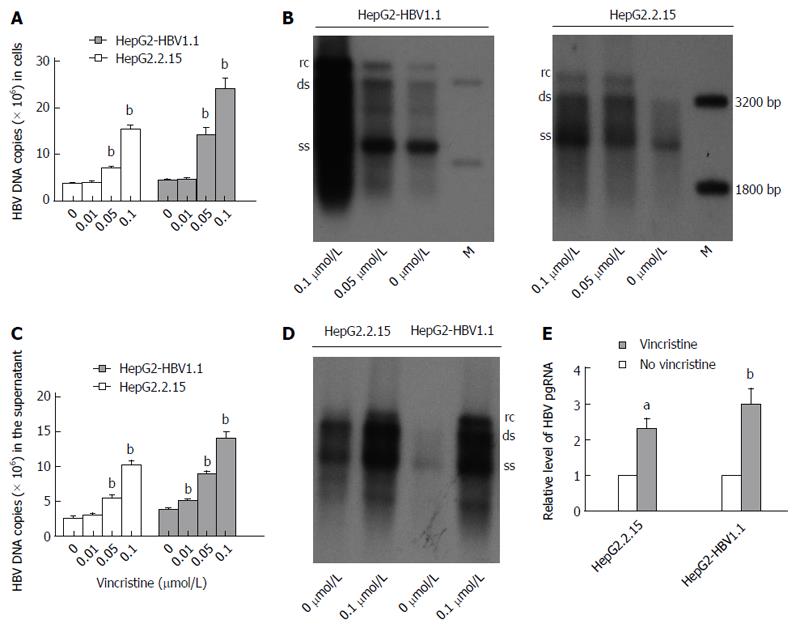
Figure 2 Dose-dependent increases in hepatitis B virus DNA and RNA in stable hepatitis B virus-expressing cell lines after treatment with vincristine.
A: Dose-dependent increase in HBV DNA in HepG2-HBV1.1 and HepG2.2.15 cells treated with vincristine based on real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis; B: Dose-dependent increase in HBV DNA in HepG2-HBV1.1 and HepG2.2.15 cells treated with vincristine based on Southern blot analysis; C: Vincristine increases HBV DNA in the supernatants of HepG2-HBV1.1 cells and HepG2.2.15 cells based on real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis; D: Vincristine increases HBV DNA in the supernatants of HepG2-HBV1.1 cells and HepG2.2.15 cells based on Southern blot analysis; E: Vincristine up-regulates HBV pgRNA based on real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis. HepG2-HBV1.1 (6 × 105/well) and HepG2.2.15 (4 × 105/well) cells were treated with 0.1 μmol/L vincristine for 24 h followed by 48 h of incubation in drug-free culture medium. HBV intermediates or total RNA were extracted 72 h after drug treatment. Values represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments, and a representative experiment is shown. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group (no vincristine). rc: Relaxed circular DNA; ds: Double-stranded DNA; ss: Single-stranded DNA. M: DNA ladder; pgRNA: Pregenome RNA.
- Citation: Xu L, Tu Z, Xu G, Hu JL, Cai XF, Zhan XX, Wang YW, Huang Y, Chen J, Huang AL. S-phase arrest after vincristine treatment may promote hepatitis B virus replication. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(5): 1498-1509
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i5/1498.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1498