Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2015; 21(5): 1468-1478
Published online Feb 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1468
Published online Feb 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1468
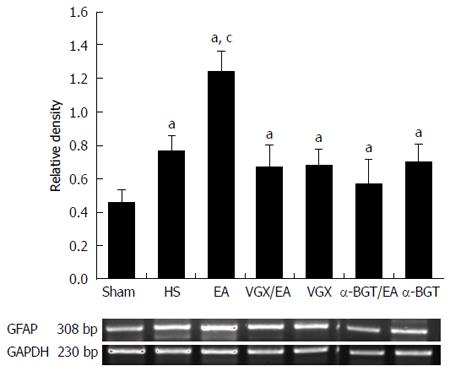
Figure 3 Electroacupuncture ST 36 alters expression of intestinal glial fibrillary acidic protein.
RT-PCR was performed on intestinal extracts obtained 6 h following injury. EA ST 36 resulted in augmented intestinal glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) mRNA expression in the EA group compared with the HS group. Abdominal vagotomy (VGX) or injection of α-bungarotoxin (BGT) abrogated the effect of EA ST36 to increase intestinal GFAP mRNA expression. aP < 0.05 vs sham group, cP < 0.05 vs HS group. EA: Electroacupuncture; HS: Hemorrhagic shock.
- Citation: Hu S, Zhao ZK, Liu R, Wang HB, Gu CY, Luo HM, Wang H, Du MH, Lv Y, Shi X. Electroacupuncture activates enteric glial cells and protects the gut barrier in hemorrhaged rats. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(5): 1468-1478
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i5/1468.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1468