Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2015; 21(48): 13447-13456
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13447
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13447
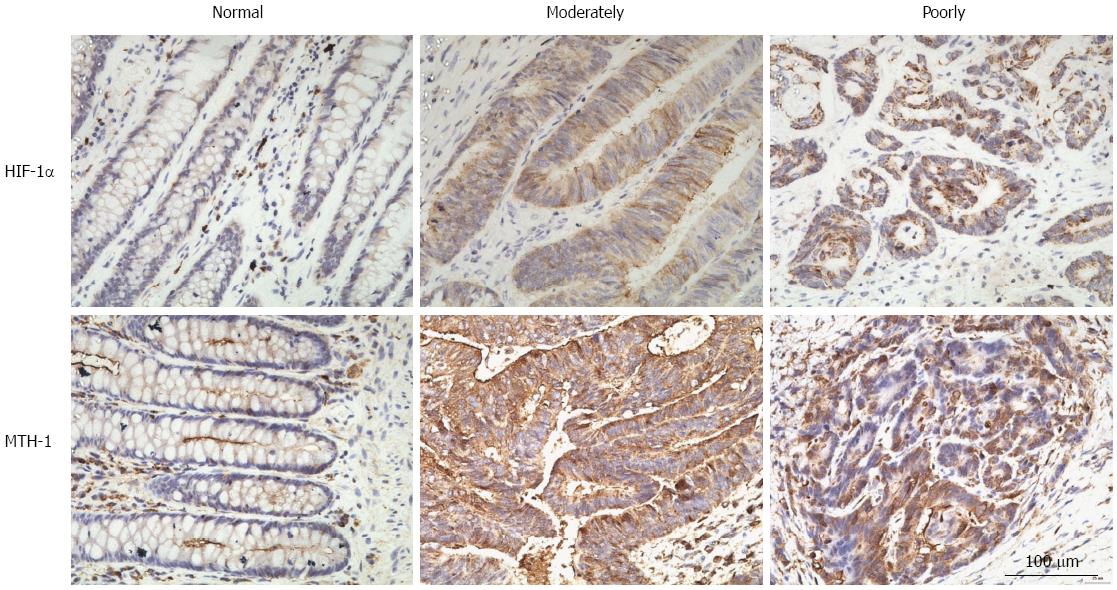
Figure 1 Images of three groups defined by immunohistochemical staining for hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and mutT homolog-1 in normally, moderately, and poorly differentiated colorectal cancer.
No HIF-1α immunoreactivity was detected in normal colorectal mucosa (A). Moderate to strong HIF-1α immunoreactivity was detected in the cytoplasm of tumor cells in moderately or poorly differentiated colorectal adenocarcinoma (B and C). MTH-1 immunoreactivity of normal colon mucosa was faint in the cytoplasm, and strong cytoplasmic immunostaining was observed in lymphoid cells (D). Moderately differentiated and poorly differentiated colorectal adenocarcinoma exhibited strong cytoplasmic staining for MTH-1 protein (E and F). Original magnification, × 400. HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; MTH-1: MutT homolog-1.
- Citation: Qiu Y, Zheng H, Sun LH, Peng K, Xiao WD, Yang H. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 modulates upregulation of mutT homolog-1 in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(48): 13447-13456
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i48/13447.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13447