Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2015; 21(48): 13438-13446
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13438
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13438
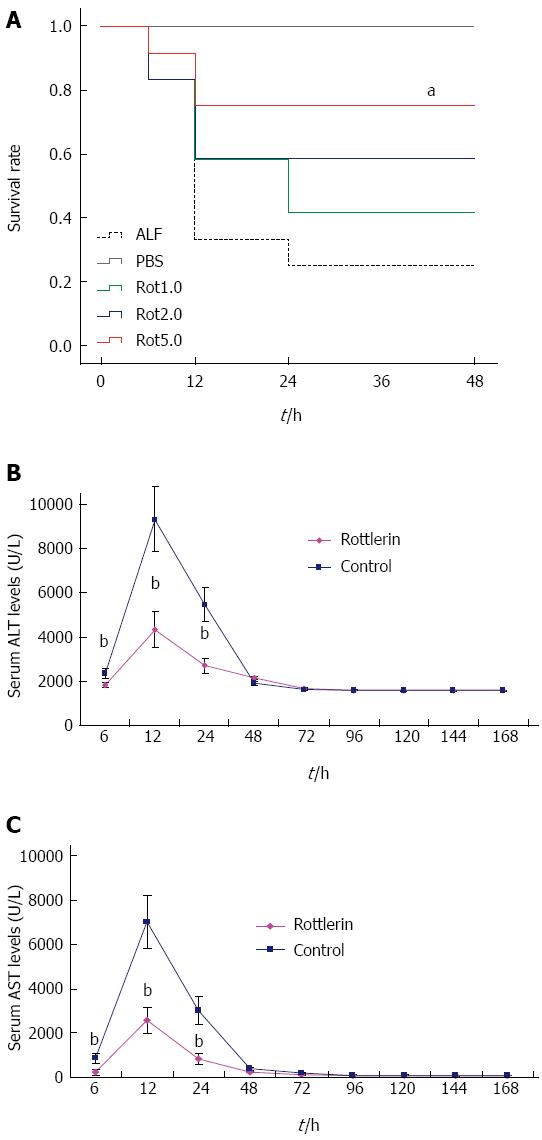
Figure 2 Inhibition of protein kinase C-δ activity with rottlerin improves survival and decreases alanine aminotransferase/aspartate aminotransferase levels in a mouse model of acute liver failure.
Animals were treated with PBS or rottlerin (0, 1, 2 and 5 μmol/L) 30 min before the induction of acute liver failure with D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide. A: Rottlerin increased the survival rate in a dose-dependent manner. Kaplan-Meier method was used to analyze the effect of rottlerin (5 μmol/L) on the survival rates of the animals. aP = 0.003 (log-rank test, F = 16.023); B and C: ALT /AST levels in peripheral blood samples collected at 6, 12, 24, 48, 72, 120, 144 and 168 h after treatment. Rottlerin treatment significantly decreased the levels of serum ALT at 6, 12 and 24 h (317.3 U/L ± 119.3 U/L, 2823.7 U/L ± 799.3 U/L, 1195.4 U/L ± 351.9 U/L vs 851.5 U/L ± 233.1 U/L, 7789.8 U/L ± 1473.7 U/L, 3943.8 U/L ± 760.2 U/L, t = 4.17, 10.26 and 11.37, respectively, bP < 0.01) and AST at 6, 12 and 24 h (221.1 U/L ± 124.3 U/L, 2579.1 U/L ± 596.4 U/L, 827.9 U/L ± 242.6 U/L vs 853.7 U/L ± 212.7 U/L, 7003.2 U/L ± 1179.6 U/L, 2991.2 U/L ± 629.1 U/L, t = 8.89, 11.59 and 11.11, respectively, bP < 0.01) vs the control group. The mean ± SE of three independent experiments is shown (error bar indicates SE). Rot: Rottlerin; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase, AST: Aspartate aminotransferase.
- Citation: Lei YC, Yang LL, Li W, Luo P. Sphingosine kinase 1 dependent protein kinase C-δ activation plays an important role in acute liver failure in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(48): 13438-13446
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i48/13438.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i48.13438