Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2015; 21(47): 13360-13367
Published online Dec 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i47.13360
Published online Dec 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i47.13360
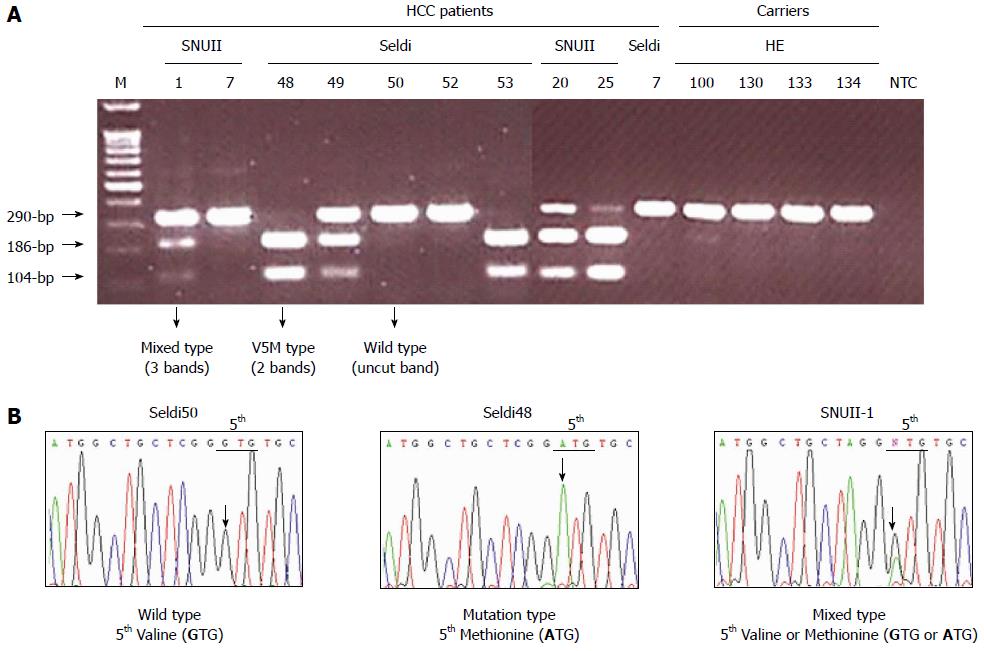
Figure 3 Application of Fok-I nested polymorphism analysis method (A) and direct sequencing analysis (B) into serum DNAs.
A: The Fok-I PRA application of nested PCR products could produce three types of PRA pattern on an agarose gel (2.5%): an undigested 290-bp from the wild type, V5(GTG); two bands of complete digestion, 186-bp and 104-bp, from the V5M mutant and three bands, an undigested one of 290-bp from the wild type and 2 digested bands, 186-bp and 104-bp, from V5M mutant. B: Direct sequencing could also produce three types: wild type only [V5(GTG)], mutation only [M5(ATG)], and mixed types with the wild type V5(GTG) and M5(ATG). The mixed types showed the mixed peaks (G and A) at the first nucleotide of the 5th codon of HBxAg (NTT). The results of the Fok-I nested PRA method were completely concordant with those obtained by direct sequencing analysis. Lane M, 100-bp DNA ladder marker.
-
Citation: Kim H, Hong SH, Lee SA, Gong JR, Kim BJ. Development of
Fok -I based nested polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis for detection of hepatitis B virus X region V5M mutation. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(47): 13360-13367 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i47/13360.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i47.13360