Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2015; 21(45): 12954-12962
Published online Dec 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12954
Published online Dec 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12954
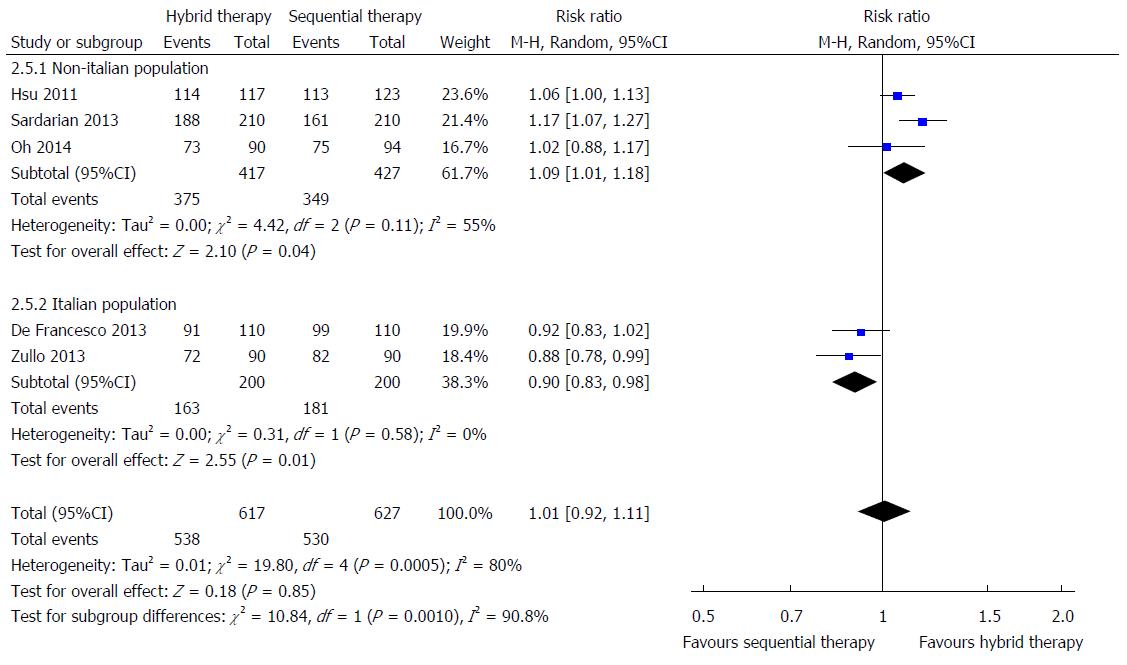
Figure 3 Forest plot of hybrid therapy vs sequential therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication; Estimates of odds ratio defined with the random effect model with 95%CI using intention-to-treat analysis.
The hybrid therapy was more effective than sequential therapy in the non-Italian population (relative risk = 1.09; 95%CI: 1.01-1.18). In contrast, the hybrid therapy was less effective than sequential therapy in the Italian population (relative risk = 0.90; 95%CI: 0.83-0.98).
-
Citation: Hsu PI, Lin PC, Graham DY. Hybrid therapy for
Helicobacter pylori infection: A systemic review and meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(45): 12954-12962 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i45/12954.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12954