Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2015; 21(45): 12814-12821
Published online Dec 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12814
Published online Dec 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12814
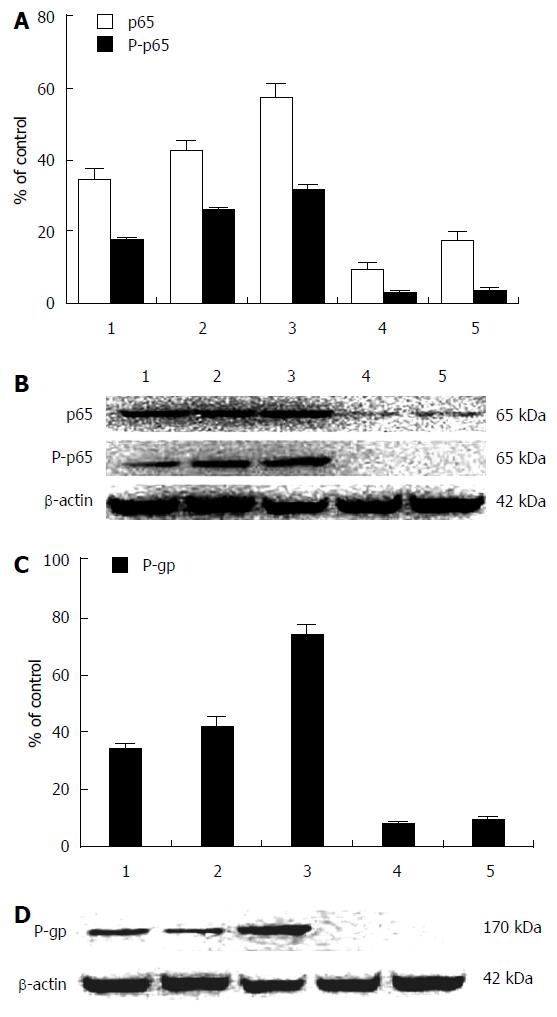
Figure 3 Downregulation of nuclear factor-κB/p65, P-p65, and P-gp expression in HepG2 cells after siRNA transfection.
1, control; 2, negative-siRNA for 48 h; 3, 0.5 μmol/L of doxorubicin for 48 h; 4, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)/p65 siRNA for 48 h; 5, 100 nmol/L of NF-κB/p65 siRNA for 24 h, then added 0.5 μmol/L of doxorubicin for another 24 h. A: The ratios of NF-κB/p65 and P-p65 expression in HepG2 cells after NF-κB/p65 siRNA transfection, data are means of independent triplicate experiments; B: The analysis of NF-κB/p65 and P-p65 expression in HepG2 cells after NF-κB/p65 siRNA transfection by western blotting; C: The relative levels of P-gp expression in HepG2 cells after NF-κB/p65 siRNA transfection, all values are means of independent triplicate experiments; D: The analysis of P-gp expression in HepG2 cells after NF-κB/p65 siRNA transfection by western blotting. The molecular weight NF-κB/p65, P-p65, and P-gp were 65 kDa, 65 kDa, and 170 kDa, respectively; and β-actin, molecular weight 42 kDa, was the control protein.
- Citation: Shi Y, Wang SY, Yao M, Sai WL, Wu W, Yang JL, Cai Y, Zheng WJ, Yao DF. Chemosensitization of HepG2 cells by suppression of NF-κB/p65 gene transcription with specific-siRNA. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(45): 12814-12821
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i45/12814.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12814