Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2015; 21(45): 12787-12799
Published online Dec 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12787
Published online Dec 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12787
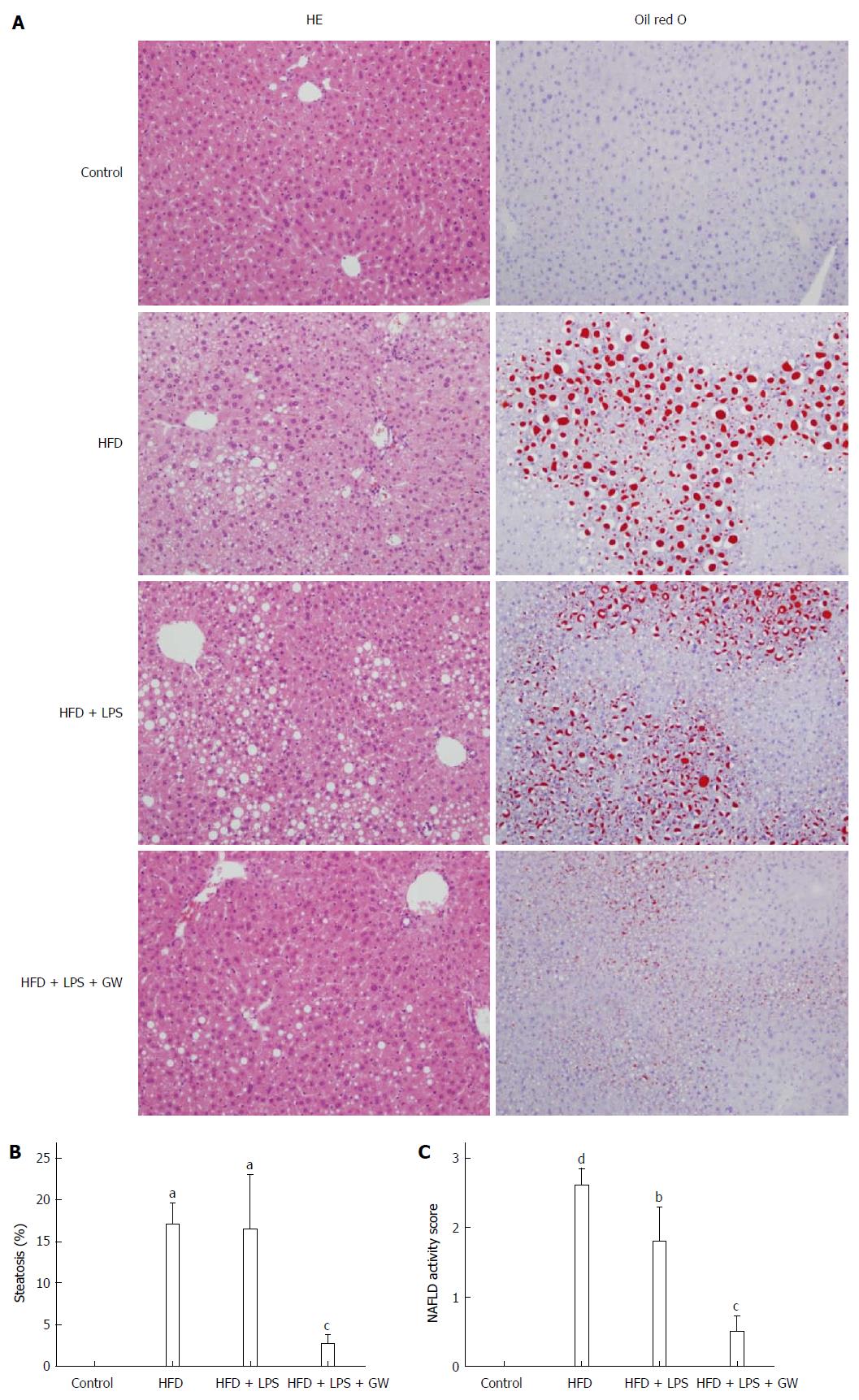
Figure 5 Histopathological features of livers in mice fed a high fat diet with or without lipopolysaccharide injection and GW501516 treatment.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and Oil Red O staining of hepatic lipid accumulation (magnification × 100). In mice fed an HFD, moderate macrovesicular steatosis (17.0%) and inflammatory cell infiltration were observed compared with the control group. The macrovesicular steatosis was improved to 2.7% following GW501516 treatment; B: Histogram of the percentage of hepatocytes showing macrovesicular fatty change; C: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) activity score. The NAFLD activity score in the GW501516-treated group was significantly lower than that in the HFD + LPS group (1.8 vs 0.5, P < 0.05). Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) (5-6 mice per group). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, and dP < 0.001 vs control group. cP < 0.05 vs the HFD + LPS group.
- Citation: Lee HJ, Yeon JE, Ko EJ, Yoon EL, Suh SJ, Kang K, Kim HR, Kang SH, Yoo YJ, Je J, Lee BJ, Kim JH, Seo YS, Yim HJ, Byun KS. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-delta agonist ameliorated inflammasome activation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(45): 12787-12799
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i45/12787.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12787