Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2015; 21(44): 12713-12721
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12713
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12713
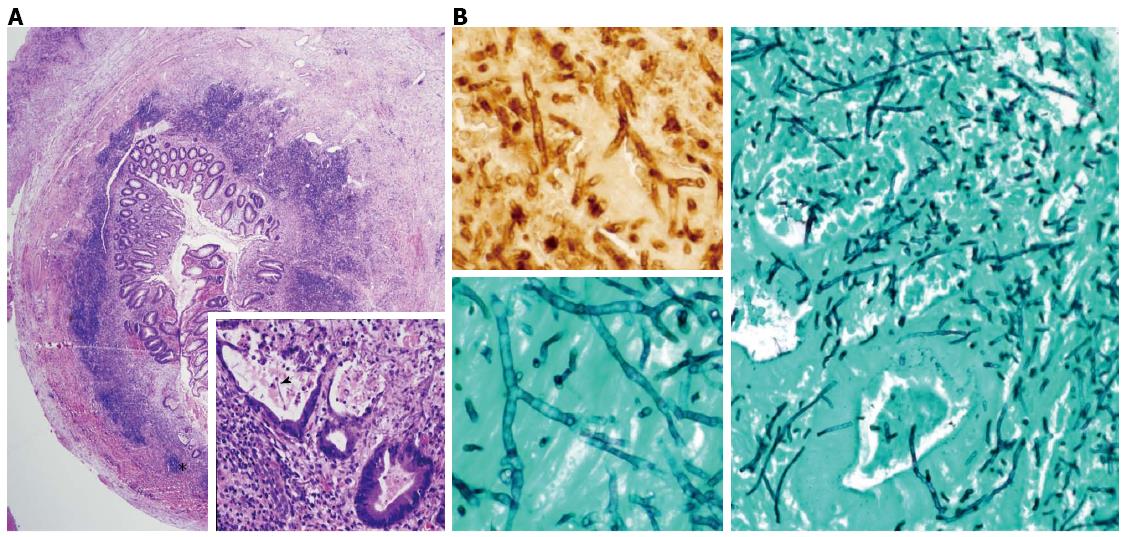
Figure 2 Photomicrograph.
A: Photomicrograph of a hematoxylin-eosin stained, full thickness, cross-section of the resected appendiceal specimen shows a thickened appendiceal wall due to a severe mixed inflammatory infiltrate (A, low power). The high power view (A-inset) of an area within the low-power view, shows one questionable fungal hyphae (arrowhead) within a gland partially destroyed by the necrotizing inflammation; B: Photomicrograph of a Grocott-Gomori methenamine-silver (GMS) nitrate stain reveals invasive, septate, hyphal forms with acutely angled branches, characteristic of Aspergilus species (B-right side-low power, B-left lower inset-high power). The hyphae are confirmed as Aspergillus species by immunohistochemistry (B-left upper inset-high power).
-
Citation: Gjeorgjievski M, Amin MB, Cappell MS. Characteristic clinical features of
Aspergillus appendicitis: Case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(44): 12713-12721 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i44/12713.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12713