Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2015; 21(44): 12593-12604
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12593
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12593
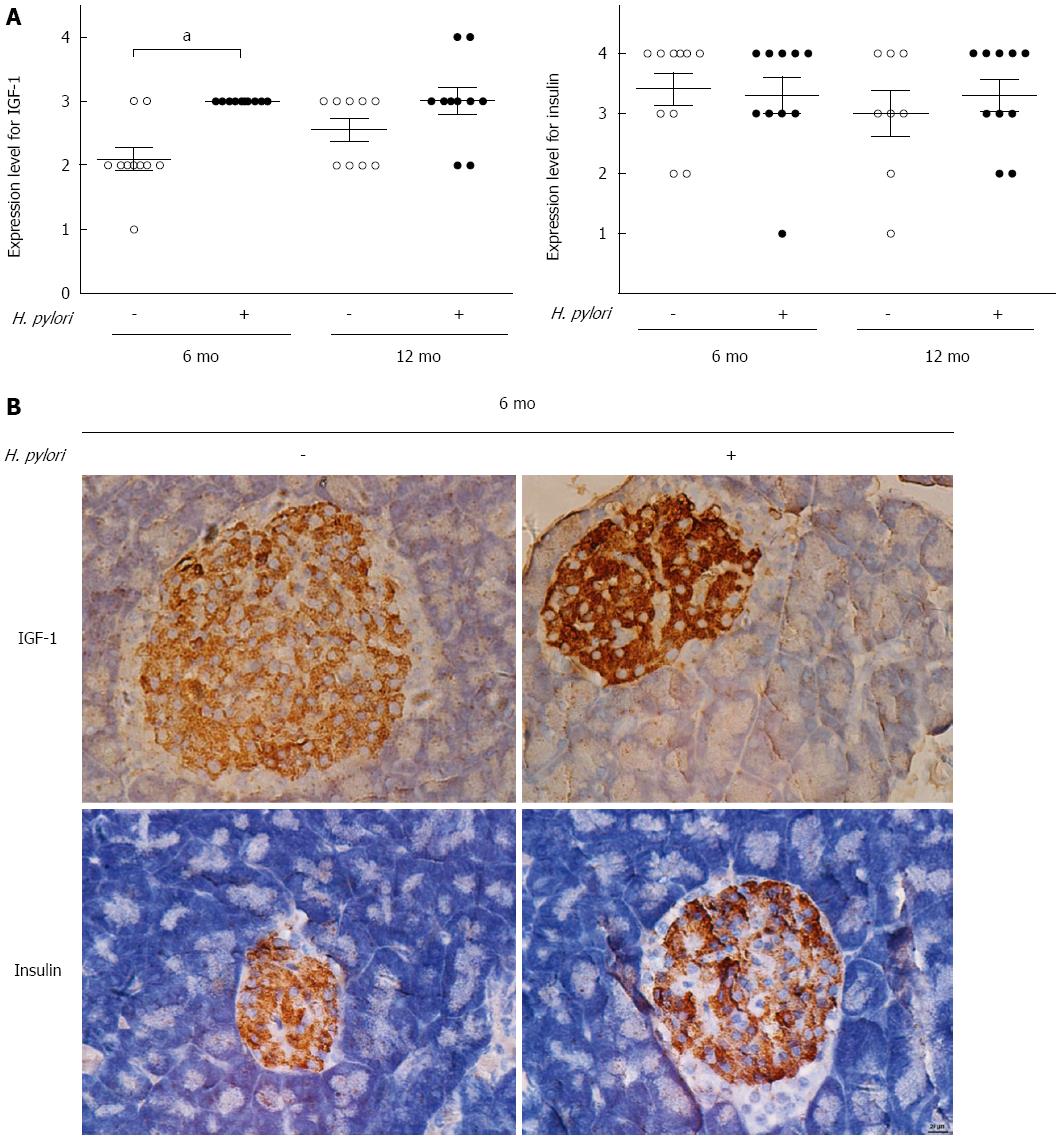
Figure 4 Effects of chronic Helicobacter pylori infection on the expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin in the pancreas of Mongolian gerbils.
A: Immunohistochemistry scores of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and insulin were determined in the control and Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) groups at 6 and 12 mo (n = 8-10). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05 between H. pylori infected mice at 6 mo and their controls concerning the expression of IGF-1; B: Representative immunohistochemical staining of IGF-1 and insulin expression in the pancreas of Mongolian gerbils at 6 mo after H. pylori infection (magnification × 400).
-
Citation: Yang Z, Li W, He C, Xie C, Zhu Y, Lu NH. Potential effect of chronic
Helicobacter pylori infection on glucose metabolism of Mongolian gerbils. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(44): 12593-12604 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i44/12593.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12593