Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2015; 21(44): 12593-12604
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12593
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12593
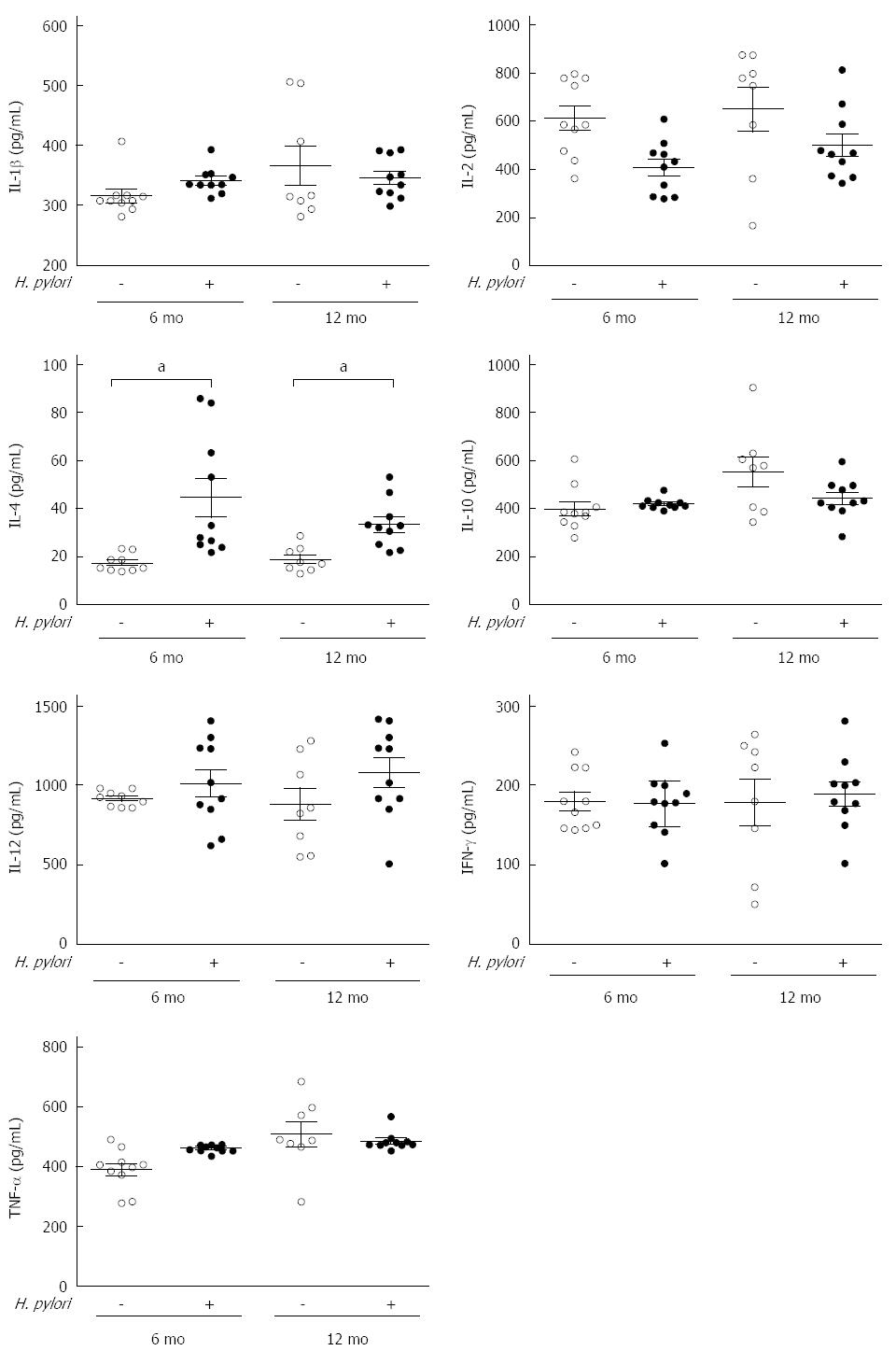
Figure 3 Effects of chronic Helicobacter pylori infection on the serum inflammatory cytokines in Mongolian gerbils at different time points.
The serum levels of cytokines including IL-1β, IL-2, IL-12, IL-4, IL-10, IFN-γ, and TNF-α were measured by ELISA at 6 and 12 mo after Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection. Data are presented as mean ± SEM from eight to ten mice per group. Cytokines were not significant different except IL-4 (aP < 0.05 between H. pylori infected mice and their controls). IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IFN: Interferon.
-
Citation: Yang Z, Li W, He C, Xie C, Zhu Y, Lu NH. Potential effect of chronic
Helicobacter pylori infection on glucose metabolism of Mongolian gerbils. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(44): 12593-12604 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i44/12593.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12593