Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2015; 21(44): 12593-12604
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12593
Published online Nov 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12593
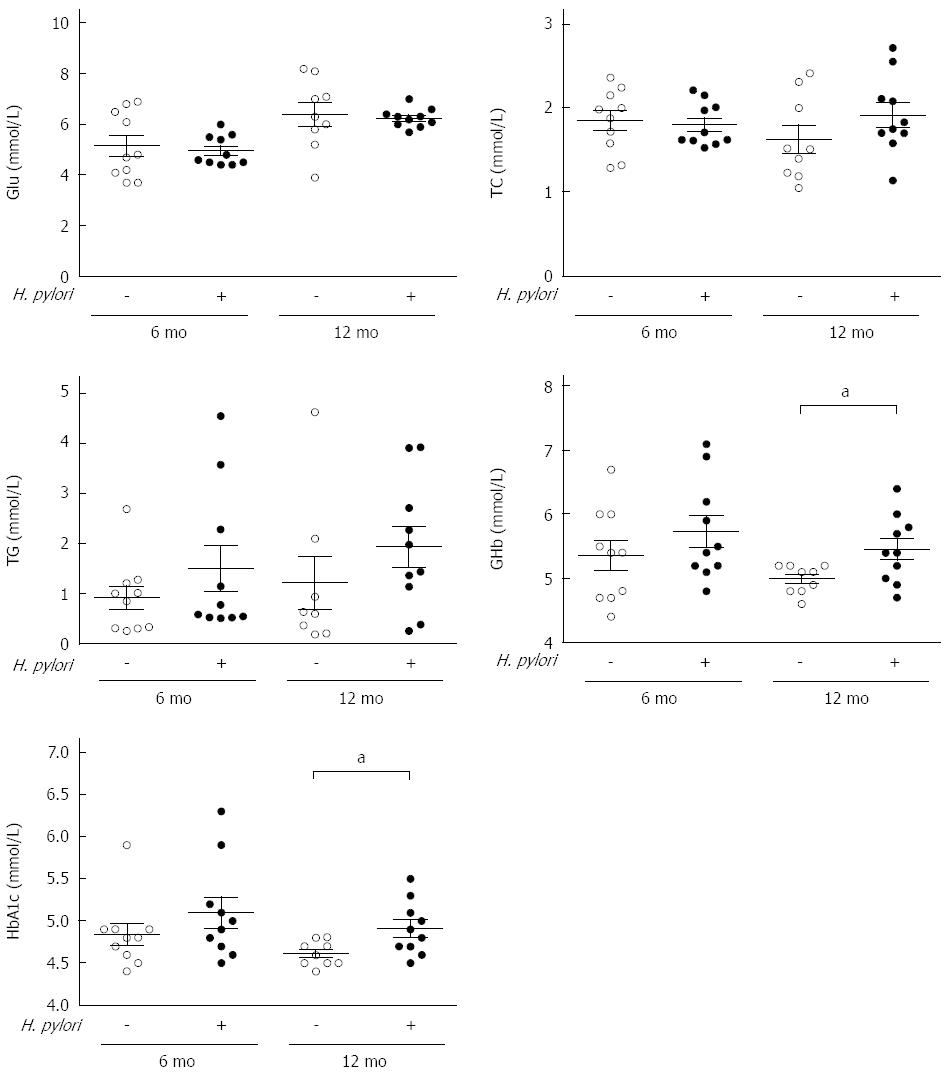
Figure 2 Measurements of serum biochemical parameters of Mongolian gerbils after Helicobacter pylori infection at different time points.
Serum concentration of fasting glucose (Glu), triacylglycerol (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and glycated hemoglobin (GHb) and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) were measured at 6 and 12 mo after Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection. Data are presented as mean ± SEM from eight to ten mice per group. aP < 0.05 between H. pylori infected mice and their controls at 12 mo concerning GHb and HbA1c.
-
Citation: Yang Z, Li W, He C, Xie C, Zhu Y, Lu NH. Potential effect of chronic
Helicobacter pylori infection on glucose metabolism of Mongolian gerbils. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(44): 12593-12604 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i44/12593.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i44.12593