Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2015; 21(43): 12392-12402
Published online Nov 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12392
Published online Nov 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12392
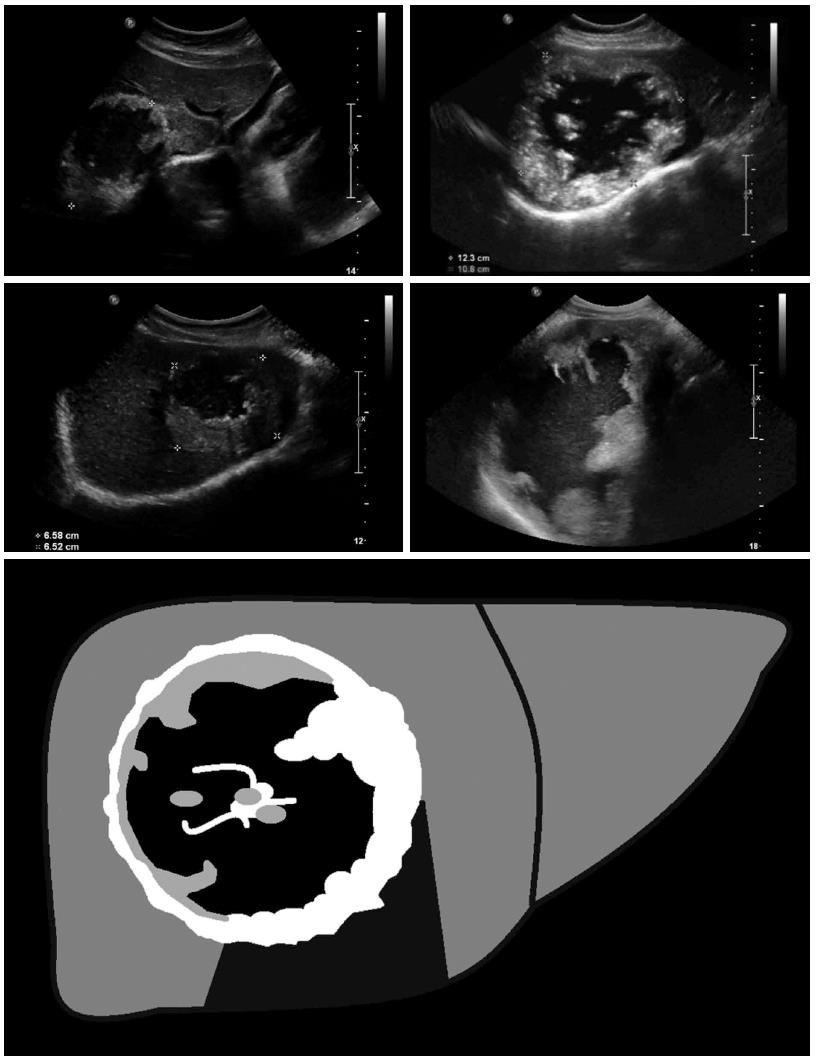
Figure 2 Pseudocystic: Pseudocystic alveolar echinococcosis lesions are primarily characterized by an hyperechoic, irregular and non-homogeneous rim that is non-vascularized at power Doppler and color-coded duplex ultrasonography.
It may appear to be > 10 mm in thickness. There is a hypo- or anechoic, often non-homogeneous central zone that may contain hyperechoic material. Pseudocystic lesions may be already present at first diagnosis and involve an entire hepatic lobe, or may develop from primary hailstorm lesions following therapy with benzimidazoles.
- Citation: Kratzer W, Gruener B, Kaltenbach TE, Ansari-Bitzenberger S, Kern P, Fuchs M, Mason RA, Barth TF, Haenle MM, Hillenbrand A, Oeztuerk S, Graeter T. Proposal of an ultrasonographic classification for hepatic alveolar echinococcosis: Echinococcosis multilocularis Ulm classification-ultrasound. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(43): 12392-12402
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i43/12392.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12392