Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2015; 21(43): 12283-12295
Published online Nov 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12283
Published online Nov 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12283
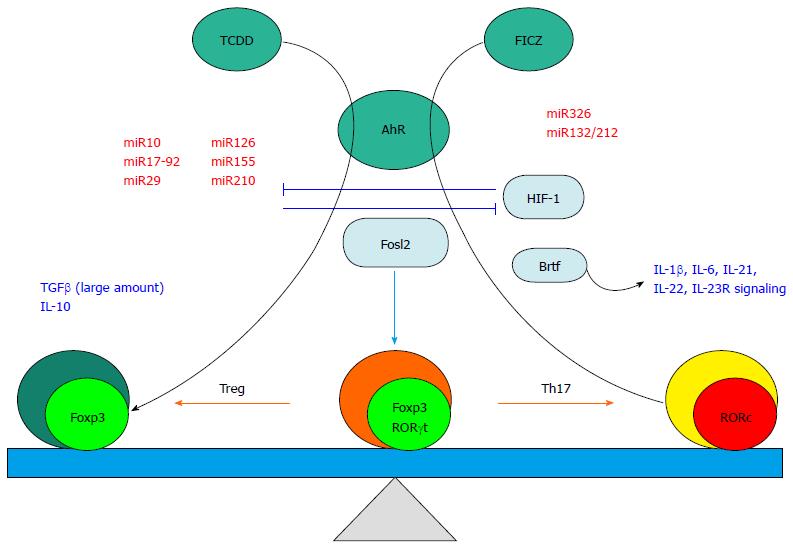
Figure 2 Factors influencing the plasticity between Treg and 17 secreting helper T subsets.
Cytokines and growth factors (shown in blue letters) may trigger transdifferentiation of the pre-committed Foxp3 expressing Treg population to RORc expressing cells. Micro RNAs (miR, shown in red letters) play a pivotal role in differentially regulating Treg/Th17 plasticity. Transcription factors (aqua ovals) direct the plasticity by positively or negatively controlling Foxp3 and/or RORc expression. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR, green circle) can promote distinct differentiation pathways in response to two pathway-specific ligands (TCDD and FICZ, Green circles) resulting in either augmentation of Foxp3 or RORc, respectively. Th17: 17 secreting helper T; FICZ: 6-formylindolo [3,2-b] carbazole; TCDD: Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; FICZ: Formylindolo [3,2-b] carbazole; AhR: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; Treg: Regulatory T cells.
- Citation: Ueno A, Ghosh A, Hung D, Li J, Jijon H. Th17 plasticity and its changes associated with inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(43): 12283-12295
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i43/12283.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i43.12283