Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2015; 21(42): 12171-12178
Published online Nov 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12171
Published online Nov 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12171
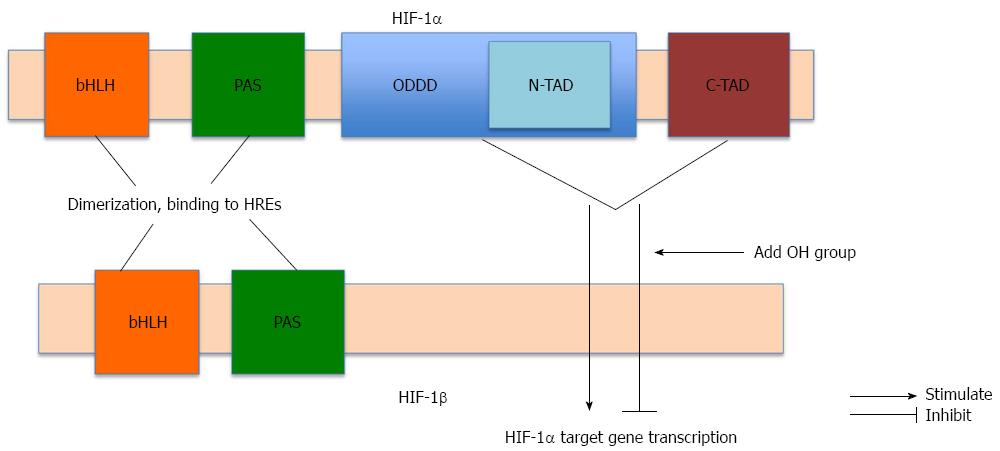
Figure 1 Structure of hypoxia-inducible factor-1.
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 is a heterodimer comprising HIF-1α and HIF-1β. Both subunits contain basic helix-loop helix (bHLH) motifs and PER-ARNT-SIM (PAS) domains needed for dimerization and binding to hypoxia response elements (HREs) in the promoter region of target regions. HIF-1α contains two transactivation domains: the NH2-terminal transactivation domain (N-TAD), located on the oxygen-dependent degradation domain (ODDD), and the carboxy-terminal transactivation domain (C-TAD). Both transactivation domains are essential for promoting HIF-1α target gene transcription. Hydroxylation of N-TAD and C-TAD of HIF-1α leads to inhibition of HIF-1α target gene transcription.
- Citation: Lin D, Wu J. Hypoxia inducible factor in hepatocellular carcinoma: A therapeutic target. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(42): 12171-12178
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i42/12171.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12171