Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2015; 21(41): 11748-11766
Published online Nov 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11748
Published online Nov 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11748
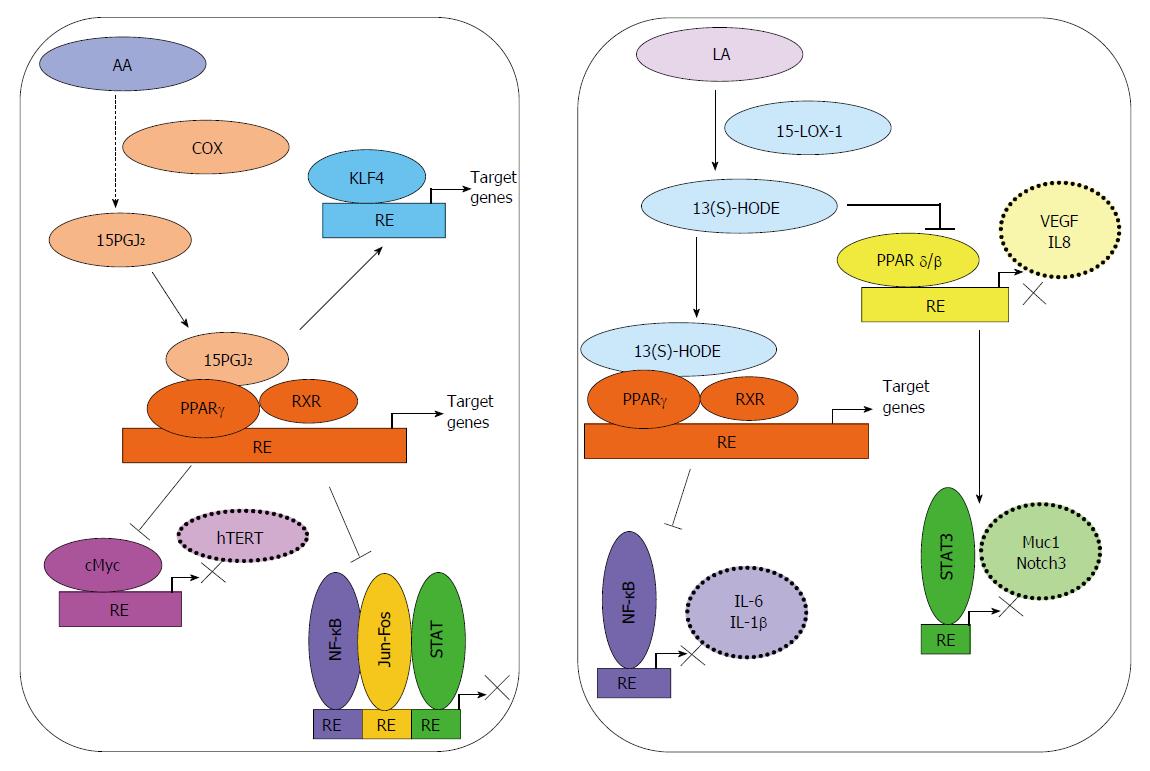
Figure 2 Activation of PPARγ by bioactive lipids can modulate signaling in progressive colorectal cancer.
15-deoxy-delta(12,14)-prostaglandin J2 (15-PGJ2), generated from arachidonic acid (AA) by the enzymatic action of COX-2, acts as a ligand for PPARγ. Co-activators such as RXR activation of tumor suppressive signaling through Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) in colorectal cancer (CRC) have also been reported. Binding to co-repressors may lead to repression of various transcription factors such as nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), AP1 (Activator Protein-1, c-Jun and c-Fos), c-Myc or STAT. 13(S)-hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid [13(S)-HODE], generated by oxygenation of linoleic acid (LA) by 15-LOX-1, can act as a ligand for PPARγ and lead to inhibition of NF-κB activity. 13(S)-HODE may also inhibit the transcriptional activities of PPARβ/δ and STAT3, and thereby reduce inflammation and angiogenesis in CRC.
- Citation: Tuncer S, Banerjee S. Eicosanoid pathway in colorectal cancer: Recent updates. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(41): 11748-11766
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i41/11748.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11748