Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2015; 21(40): 11304-11311
Published online Oct 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i40.11304
Published online Oct 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i40.11304
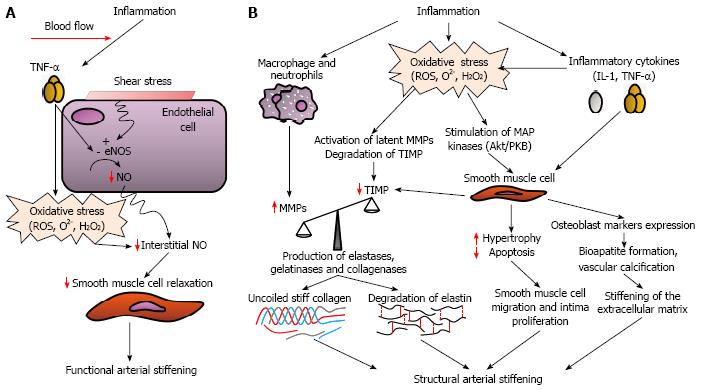
Figure 4 Potential mechanisms by which inflammation can induce functional (A) and structural (B) arterial stiffening.
eNOS: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase; H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; IL-1: Interleukin-1; MMPs: Matrix metalloproteinases; NO: Nitric oxide; O2-: Superoxide; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TIMP: Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
- Citation: Zanoli L, Rastelli S, Inserra G, Castellino P. Arterial structure and function in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(40): 11304-11311
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i40/11304.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i40.11304