Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2015; 21(4): 1334-1343
Published online Jan 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i4.1334
Published online Jan 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i4.1334
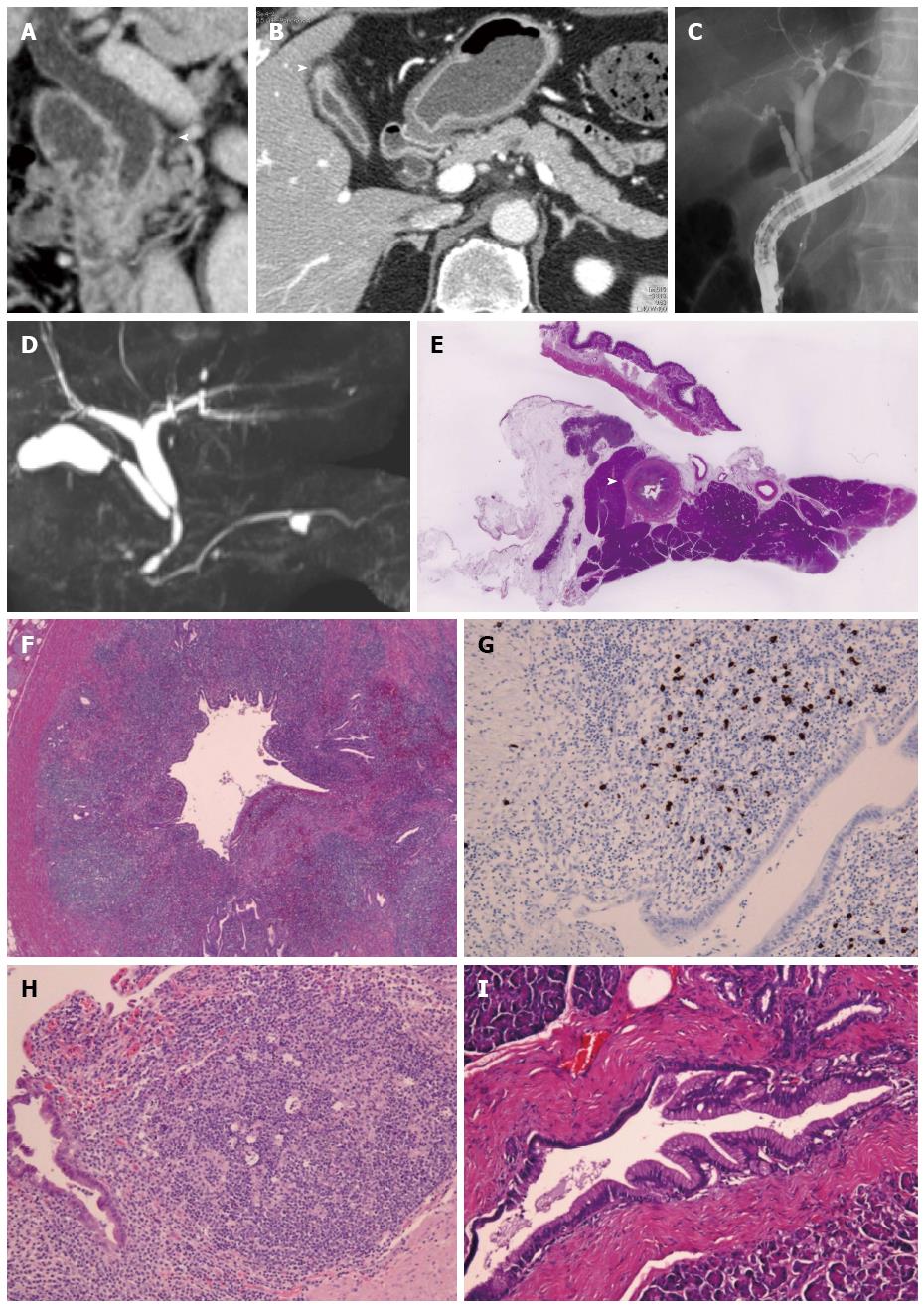
Figure 3 Imaging and pathological findings of Case 2.
A: Long segmental wall thickness in the middle and lower extrahepatic bile duct on abdominal computed tomography (arrowhead); B: Wall thickness of the fundus of gall bladder (arrowhead) and normal size of the pancreas; C: Long segmental stenosis in the middel and lower extrahepatic bile duct on endoscopic retrograde cholangiography; D: Normal main pancreatic duct except a pancreatic cyst on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography; E: Bile duct wall thicking (arrow head) and no inflammation of pancreas tissue in surgical specimen (HE × 1); F: Abundant infiltration of lymphocytes and plasma cells in the bile duct wall (HE × 200); G: Abundant infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells in the bile duct wall (IgG4 staining × 400); H: Numerous lymphocytes and plasma cells in the wall of gall bladder (HE × 400); I: Normal pancreatic tissue in adjacent pancreas (HE × 400).
- Citation: Nakazawa T, Ikeda Y, Kawaguchi Y, Kitagawa H, Takada H, Takeda Y, Makino I, Makino N, Naitoh I, Tanaka A. Isolated intrapancreatic IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(4): 1334-1343
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i4/1334.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i4.1334