Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2015; 21(4): 1148-1157
Published online Jan 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i4.1148
Published online Jan 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i4.1148
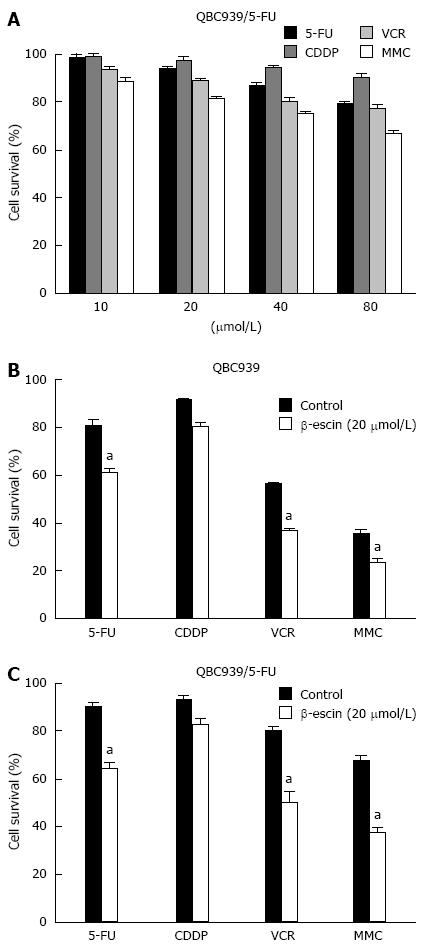
Figure 1 β-escin enhanced the sensitivity of cholangiocarcinoma cells to chemotherapeutic drugs.
A: MDR cell line QBC939/5-FU cells were treated with different concentrations of 5-FU, CDDP, VCR, and MMC for 24 h. Cell viability measured by MTT assays; B-C: Effects of β-escin (20 μmol/L) in combination with chemotherapeutics (40 μmol/L) on QBC939 cells and QBC939/5-FU cells. Cell viability measured by MTT assays after treatment for 24 h. aP < 0.05 vs control. MDR: Multidrug resistance; MTT: 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide; 5-FU: 5-fluorouracil; VCR: Vincristine sulfate; MMC: Mitomycin C; CDDP: Cisplatin.
- Citation: Huang GL, Shen DY, Cai CF, Zhang QY, Ren HY, Chen QX. β-escin reverses multidrug resistance through inhibition of the GSK3β/β-catenin pathway in cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(4): 1148-1157
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i4/1148.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i4.1148