Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2015; 21(37): 10609-10620
Published online Oct 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i37.10609
Published online Oct 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i37.10609
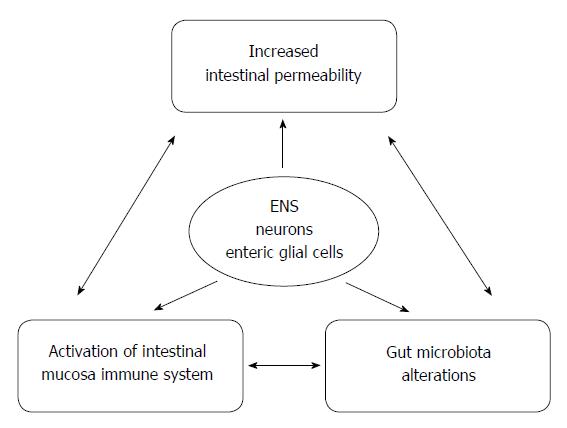
Figure 1 The link between gut dysbiosis, intestinal permeability and neurological dysfunction.
There is a close mutual relationship between gut dysbiosis, intestinal permeability and gut inflammation. The enteric nervous system (ENS) is a key player participating in these interactions. Changes in the intestinal permeability may promote translocation of bacteria and endotoxins across the epithelial barrier inducing immunological response associated with the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The activation of both enteric neurons and glial cells may result in neurological dysfunction spreading along the brain-gut axis.
- Citation: Mulak A, Bonaz B. Brain-gut-microbiota axis in Parkinson's disease. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(37): 10609-10620
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i37/10609.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i37.10609