Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2015; 21(35): 10137-10149
Published online Sep 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i35.10137
Published online Sep 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i35.10137
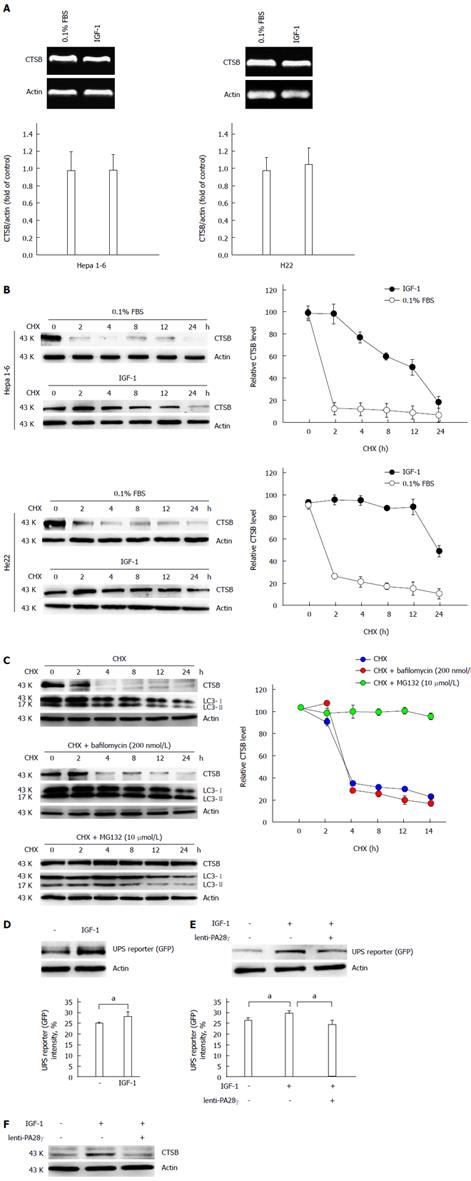
Figure 4 IGF-1 impeded cathepsin B degradation by inhibiting ubiquitin-proteasome system activity.
A: IGF-1 did not affect the mRNA level of cathepsin B (CTSB). Hep1-6 and H22 cells were treated with IGF-1 for 12 h. The mRNA expression levels of CTSB and actin were determined by RT-PCR; B: IGF-1 impeded CTSB degradation. Hep1-6 and H22 cells were incubated with CHX (10 g/mL) for the indicated time points after IGF-1 stimulation. CTSB and actin protein levels were detected by immunoblotting; C: CTSB degradation is dependent on ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) activity. Hep1-6 cells were treated with CHX plus an autophagy inhibitor (bafilomycin, 200 nmol/L) or UPS inhibitor (MG132, 10 μmol/L) at the indicated time points. Cell lysates were isolated for immunoblotting; D: IGF-1 inhibited UPS activity. Hep1-6 cells were transfected with UbG76V-GFP plasmid. At 24 h after the cells were transfected, they were treated with IGF-1 for another 12 h, and UbG76V-GFP expression was detected immunoblotting with anti-GFP antibody or by flow cytometry; E: PA28γ overexpression reversed the IGF-1-induced inhibition of UPS activity. Hepa 1-6 cells were infected with lentivirus containing PA28γ. After 24 h, the cells were treated with IGF-1 for 12 h. UbG76V-GFP expression was detected by immunoblotting with anti-GFP antibody or by flow cytometry; F: PA28γ overexpression recovered CTSB degradation. Hepa 1-6 cells were infected with lentivirus containing PA28γ. After 24 h, the cells were treated with IGF-1 for 12 h, and CTSB expression was detected by immunoblotting with anti-CTSB antibody. Data are presented as the mean ± SE of 3 independent assays. aP < 0.05.
-
Citation: Lei T, Ling X. IGF-1 promotes the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma
via the inhibition of proteasome-mediated cathepsin B degradation. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(35): 10137-10149 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i35/10137.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i35.10137