Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2015; 21(35): 10137-10149
Published online Sep 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i35.10137
Published online Sep 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i35.10137
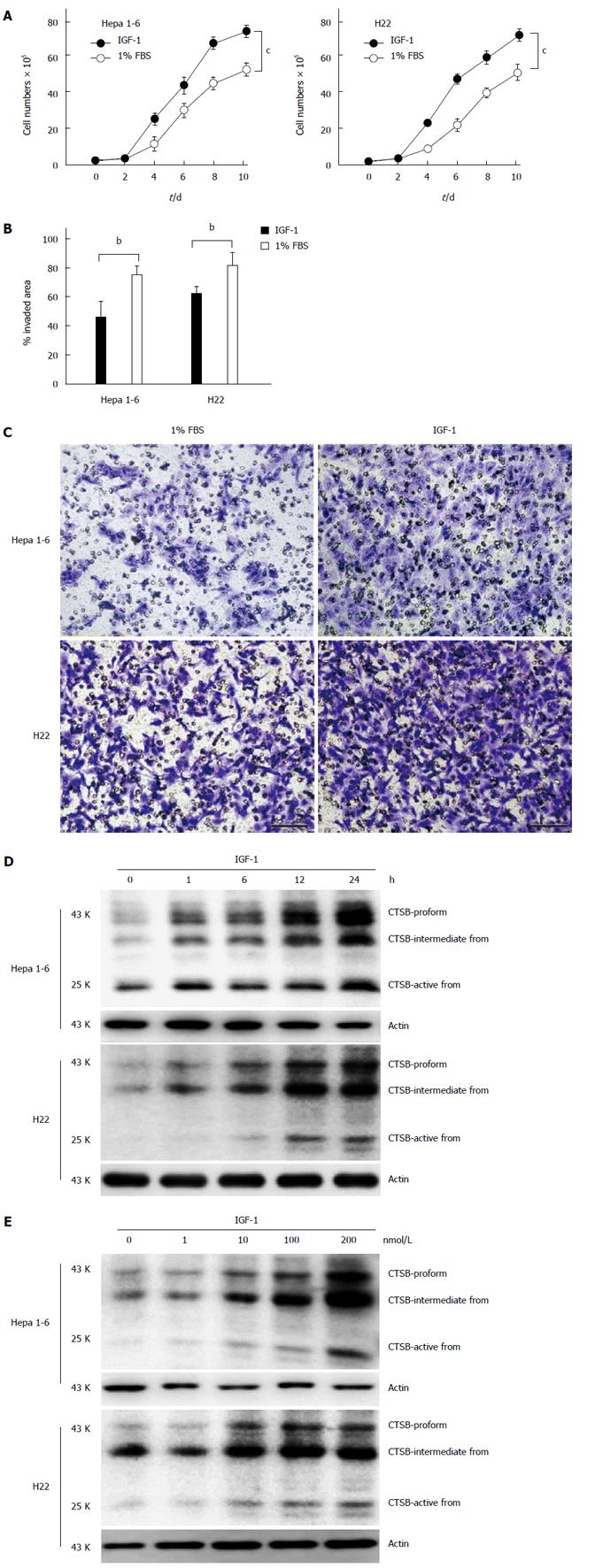
Figure 1 Cathepsin B mediates the IGF-1-induced hepatocellular carcinoma-promoting effect.
A: Hepa 1-6 and H22 cells were treated with IGF-1 (100 nmol/L) for 10 d. The data are presented as representative growth curves; B: Wound healing assay of Hepa 1-6 and H22 cells treated with IGF-1 for 24 h; C: IGF-1 induced Hepa 1-6 and H22 cell invasion. In total, 1 × 105 Hepa 1-6 and H22 cells that had been treated with IGF-1 for 24 h were allowed to invade through Transwell inserts (8 μm) coated with Matrigel. The cells on the lower surface of the chambers were stained and imaged. The data are presented as a representative Transwell assay (scale bar, 20 μm); D and E: Hepa 1-6 and H22 cells were treated with IGF-1 (100 nmol/L) for the indicated times or treated with different IGF-1 concentrations for 12 h. CTSB expression was determined by immunoblotting. The data are presented as representative immunoblots. Student’s t-test. bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001, IGF-1 group vs 1% FBS group.
-
Citation: Lei T, Ling X. IGF-1 promotes the growth and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma
via the inhibition of proteasome-mediated cathepsin B degradation. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(35): 10137-10149 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i35/10137.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i35.10137