Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2015; 21(34): 9887-9899
Published online Sep 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9887
Published online Sep 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9887
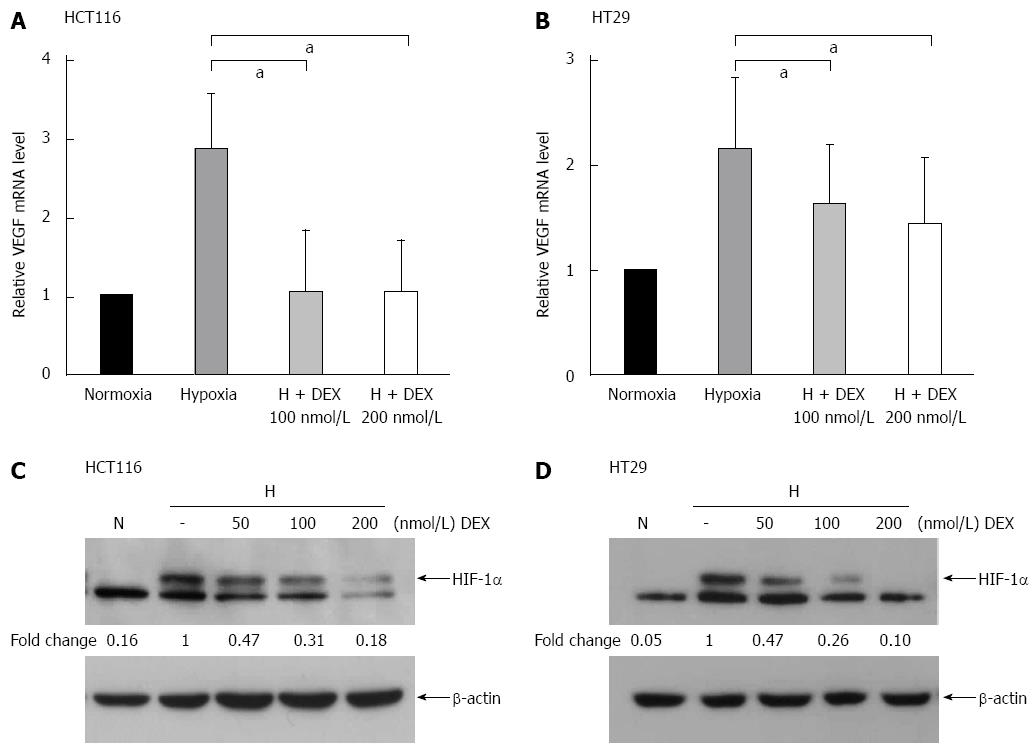
Figure 1 Effects of dexamethasone on vascular endothelial growth factor and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in HCT116 and HT29 cells under hypoxia.
A and B: RNA was extracted from cells treated with DEX (100, 200 nmol/L) and/or hypoxia for 24 (A) or 72 h (B). VEGF mRNA expression was analyzed by qPCR and normalized to glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase. DEX-treated HCT116 and HT29 cells in hypoxic conditions displayed the reduction of VEGF mRNA level; C and D: HIF-1α and β-actin protein expression in cells treated with DEX (50, 100, and 200 nmol/L) and/or hypoxia for 24 h was assessed by western blot analysis. HIF-1α protein level was inhibited in HCT116 and HT29 cells treated with DEX under hypoxic conditions. The error bar represents the standard deviation. aP < 0.05 vs hypoxia-only group. DEX: Dexamethasone; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; HIF-1α: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; N: Normoxia; H: Hypoxia; qPCR: Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
- Citation: Kim JH, Hwang YJ, Han SH, Lee YE, Kim S, Kim YJ, Cho JH, Kwon KA, Kim JH, Kim SH. Dexamethasone inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colon cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(34): 9887-9899
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i34/9887.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9887