Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2015; 21(33): 9808-9816
Published online Sep 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9808
Published online Sep 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9808
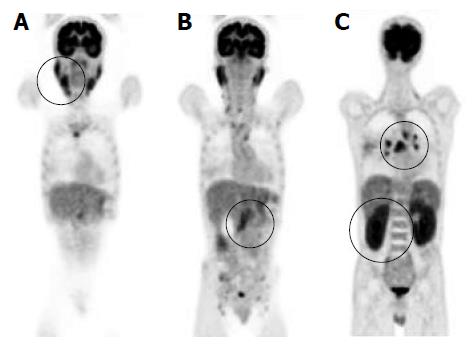
Figure 1 Findings of fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography.
Positron emission tomography revealed high fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in various organs (uptake is indicated by circles). A: Submandibular glands (SUVmax 5.6) and parotid glands (SUVmax 5.8); B: Pancreas (SUVmax 4.2); C: Bilateral hilar of lymph nodes (SUVmax 7.3) and both kidneys (SUVmax 6.2).
- Citation: Nakano E, Kanno A, Masamune A, Yoshida N, Hongo S, Miura S, Takikawa T, Hamada S, Kume K, Kikuta K, Hirota M, Nakayama K, Fujishima F, Shimosegawa T. IgG4-unrelated type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(33): 9808-9816
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i33/9808.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9808