Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2015; 21(33): 9727-9735
Published online Sep 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9727
Published online Sep 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9727
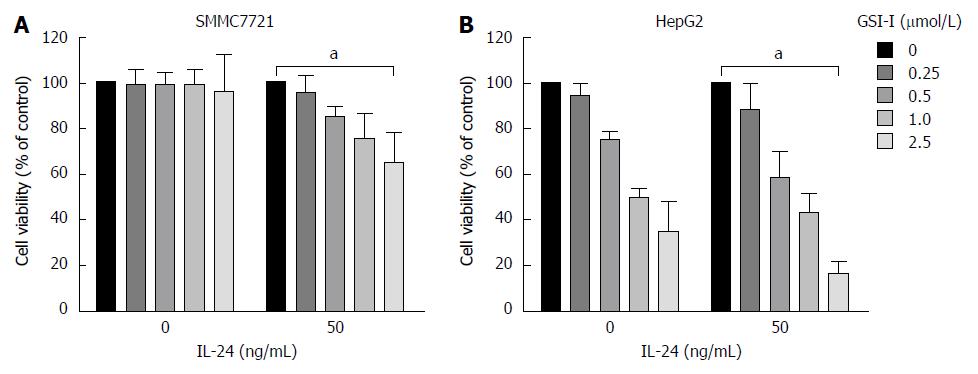
Figure 1 γ-secretase inhibitor-I/interleukin-24 combined treatment induces apoptotic cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
A: Cytotoxic effects exerted on SMMC7721 cells by γ-secretase inhibitor-I (GSI-I) employed alone or in combination with recombinant interleukin (IL)-24. After treatment for 24 h cell viability was evaluated by MTT assay as reported in Materials and Methods; B: Cytotoxic effects exerted on HepG2 cells by GSI-I employed alone or in combination with recombinant IL-24. After treatment for 24 h cell viability was evaluated by MTT assay as reported in Materials and Methods. The data represent mean ± SD; aP < 0.05 vs control cells.
- Citation: Han B, Liu SH, Guo WD, Zhang B, Wang JP, Cao YK, Liu J. Notch1 downregulation combined with interleukin-24 inhibits invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(33): 9727-9735
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i33/9727.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9727