Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2015; 21(32): 9566-9576
Published online Aug 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9566
Published online Aug 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9566
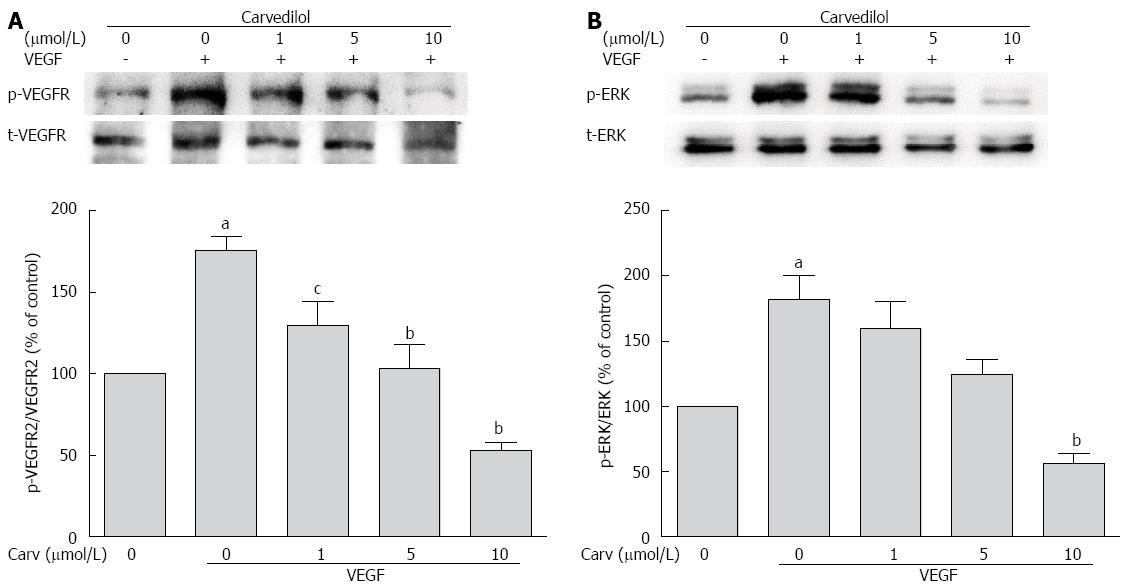
Figure 6 Effect of carvedilol on vascular endothelial growth factor angiogenic signaling.
HUVECs were treated with VEGF (50 ng/mL) for 2 h in the presence or absence of different concentrations of carvedilol. Cell lysates were processed as indicated in the Materials and Methods. p-VEGFR2/VEGFR2 (A) and p-ERK/ERK (B) levels (n = 3, aP < 0.05 vs control, cP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs VEGF alone). ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase.
- Citation: Ding Q, Tian XG, Li Y, Wang QZ, Zhang CQ. Carvedilol may attenuate liver cirrhosis by inhibiting angiogenesis through the VEGF-Src-ERK signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(32): 9566-9576
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i32/9566.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i32.9566