Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2015; 21(30): 9189-9208
Published online Aug 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9189
Published online Aug 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9189
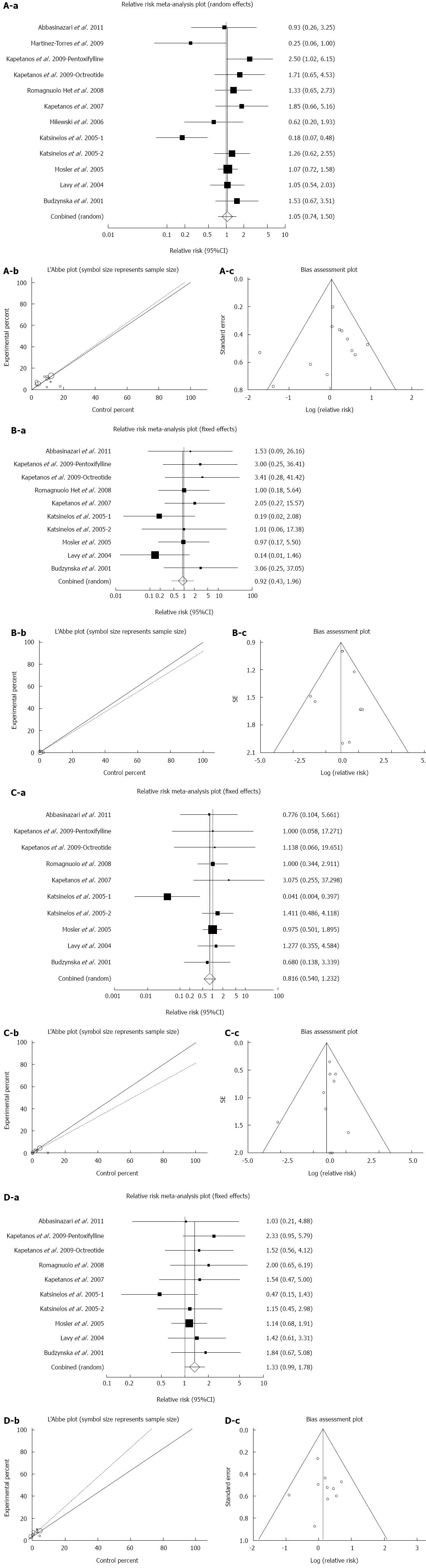
Figure 5 Effect of antioxidants compared with placebo therapy on incidence.
Individual and pooled relative risk (A-a), heterogeneity indicators for (A-b), and publication bias indicators for (A-c) the outcome of “all types of PEP” in the studies considering antioxidants compared to placebo therapy in 1849 patients undergoing ERCP; individual and pooled relative risk (B-a); Heterogeneity indicators (B-b); and publication bias indicators (B-c) for the outcome of “severe PEP” in the studies considering antioxidants compared to placebo therapy in 1709 patients undergoing ERCP; individual and pooled relative risk (C-a); heterogeneity indicators for (C-b); publication bias indicators (C-c) for the outcome of “moderate PEP” in the studies considering antioxidants compared to placebo therapy in 1709 patients undergoing ERCP; individual and pooled relative risk (D-a); heterogeneity indicators (D-b); publication bias indicators (D-c) for the outcome of “mild PEP” in the studies considering antioxidants compared to placebo therapy in 1709 patients undergoing ERCP. PEP: Post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
- Citation: Gooshe M, Abdolghaffari AH, Nikfar S, Mahdaviani P, Abdollahi M. Antioxidant therapy in acute, chronic and post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(30): 9189-9208
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i30/9189.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9189