Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2015; 21(30): 9093-9102
Published online Aug 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9093
Published online Aug 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9093
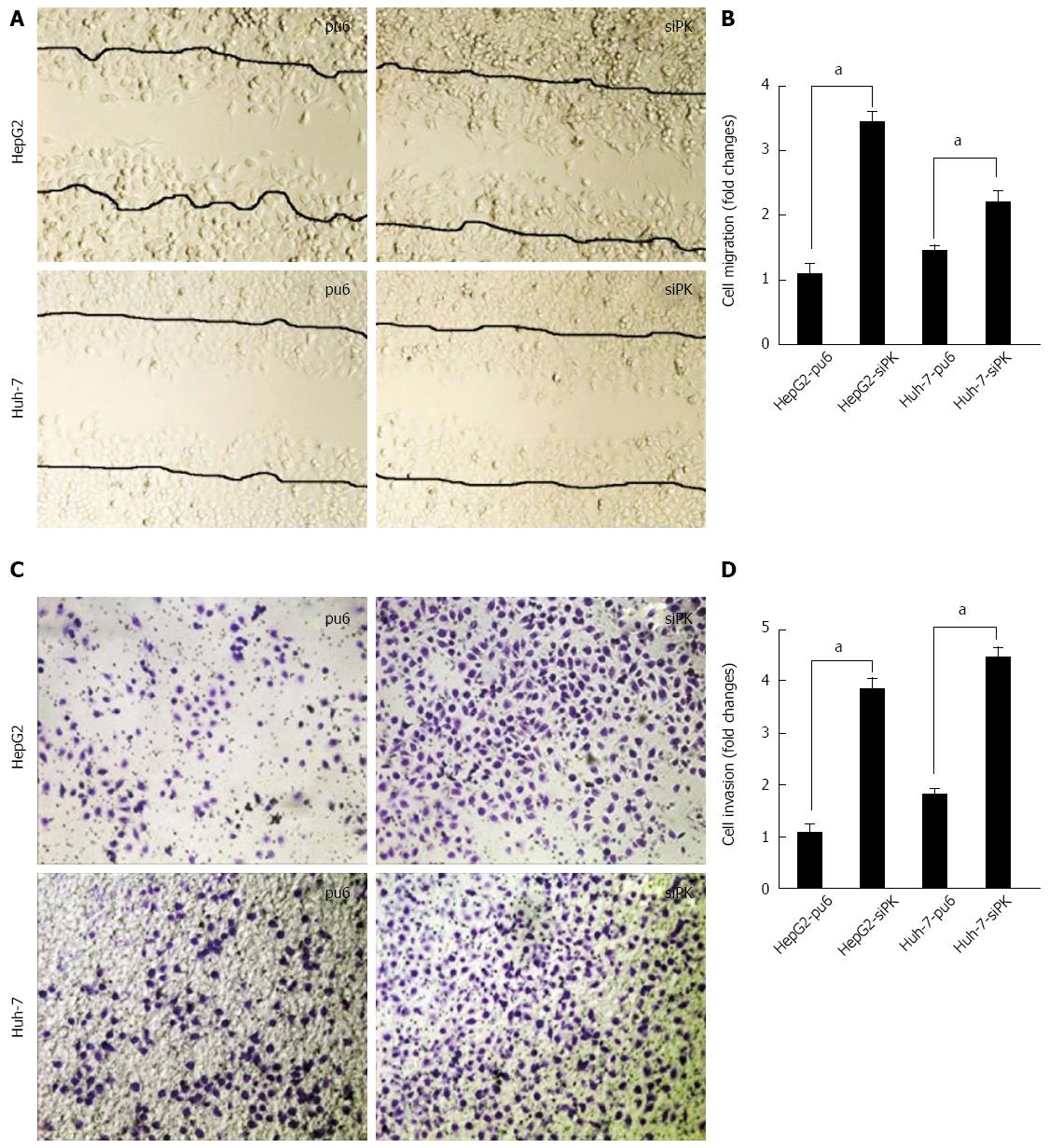
Figure 2 Knockdown of pyruvate kinase M2 isoform promoted the migration and invasion of HepG2 and Huh-7 cells upon epidermal growth factor stimulation.
A: A cross-shaped wound was created in the monolayer, and stably transfected HepG2 and Huh-7 cells were cultured for an additional 24 h with epidermal growth factor (EGF) (50 ng/mL). Representative images of the wounded region are shown; B: The results of the migration assay are also shown as graphs (aP < 0.05); C: The invasion potential of the HepG2 and Huh-7 stable cells was assessed using the BD transwell chamber assay with 50 ng/mL EGF in the lower chamber for 36 h. The cells that migrated to the lower side of the filter were stained, photographed, and counted; D: The data are expressed as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments, aP < 0.05 between groups.
- Citation: Chen YL, Song JJ, Chen XC, Xu W, Zhi Q, Liu YP, Xu HZ, Pan JS, Ren JL, Guleng B. Mechanisms of pyruvate kinase M2 isoform inhibits cell motility in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(30): 9093-9102
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i30/9093.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i30.9093