Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2015; 21(3): 759-785
Published online Jan 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.759
Published online Jan 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.759
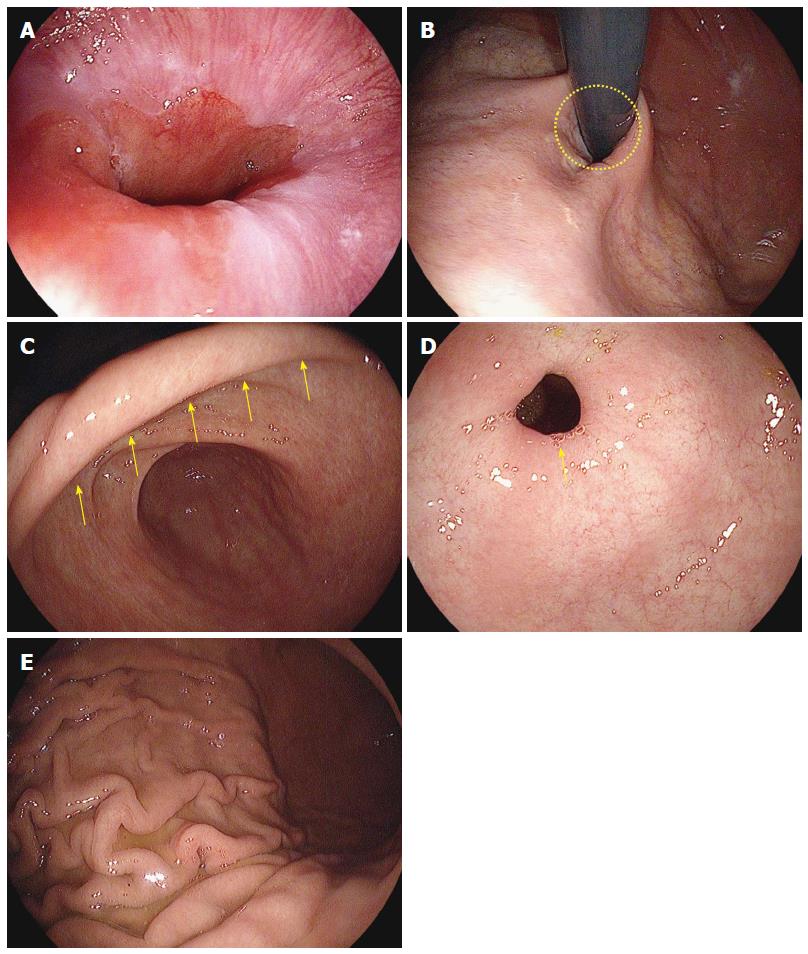
Figure 16 Intubation from stomach to duodenal bulb.
A: Gastroesophageal junction (GEJ). In absence of hiatal hernia, the GEJ lies next to the cardia; B: Gastric cardia observed in retroflexion of the scope. Likewise, in the absence of hiatal hernia, the gastric cardia is located next to the gastroesophageal junction; C: Gastric angle. If the distal tip of the scope is deflected upward in the distal antrum, the gastric angle (arrow marks) in an arched shape will be observed; D: Pyloric ring. The pyloric ring is usually observed to have a circular shape (arrow mark); E: Gastric fold. For a patient who does not have a severe case of atrophic gastritis, the gastric fold serves as a landmark to distinguish the body of stomach from the antrum of stomach.
- Citation: Lee SH, Park YK, Cho SM, Kang JK, Lee DJ. Technical skills and training of upper gastrointestinal endoscopy for new beginners. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(3): 759-785
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i3/759.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.759