Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2015; 21(28): 8615-8628
Published online Jul 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i28.8615
Published online Jul 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i28.8615
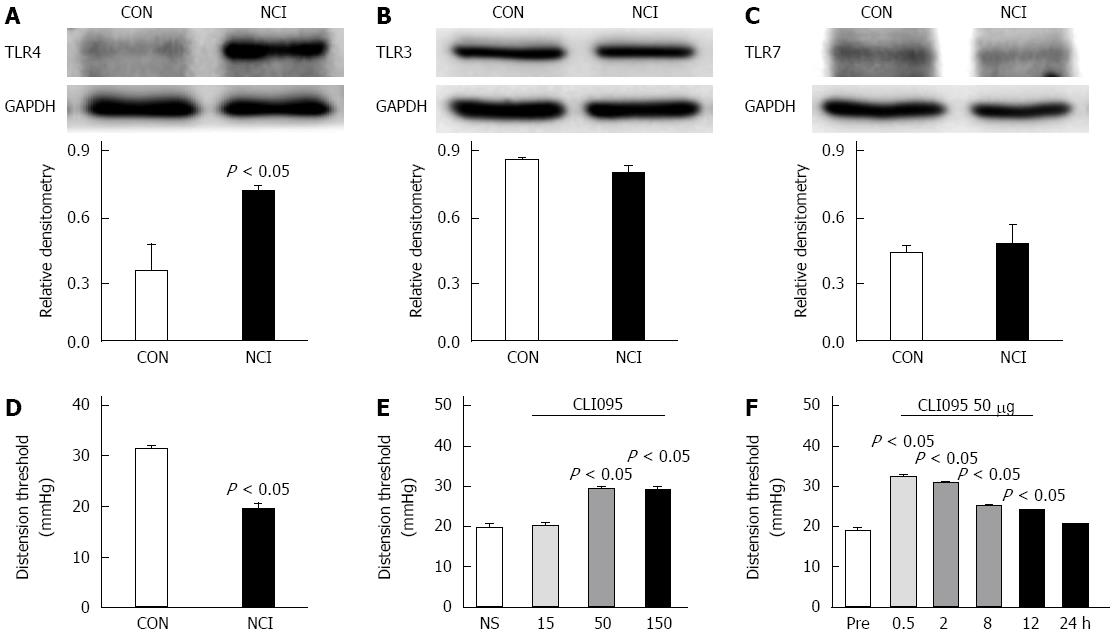
Figure 3 Neonatal colonic inflammation upregulates toll-like receptor 4 expression in dorsal root ganglia of rats with visceral hypersensitivity.
Western blotting analysis for TLR4 (A), TLR3 (B), TLR7 (C) and GAPDH (A, B, C) protein levels in T13-L2 DRGs from CON or NCI rats (n = 4 for each group); D: NCI significantly reduced the distension threshold of rats at the age of 6 wk (n = 8 for each group); E: The TLR4 selective inhibitor CLI095 significantly increased the distention threshold of NCI rats at doses of 50 and 150 μg/kg body weight. n = 8 for each group, Tukey’s post hoc test following one-way ANOVA, compared with NS; F: The time course of the effects of CLI095 at a dose of 50 μg/kg body weight, Tukey’s post hoc test following one-way repeated ANOVA. CON: Control; TLR: Toll-like receptor; NCI: Neonatal colonic inflammation.
- Citation: Yuan B, Tang WH, Lu LJ, Zhou Y, Zhu HY, Zhou YL, Zhang HH, Hu CY, Xu GY. TLR4 upregulates CBS expression through NF-κB activation in a rat model of irritable bowel syndrome with chronic visceral hypersensitivity. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(28): 8615-8628
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i28/8615.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i28.8615