Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2015; 21(27): 8340-8351
Published online Jul 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8340
Published online Jul 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8340
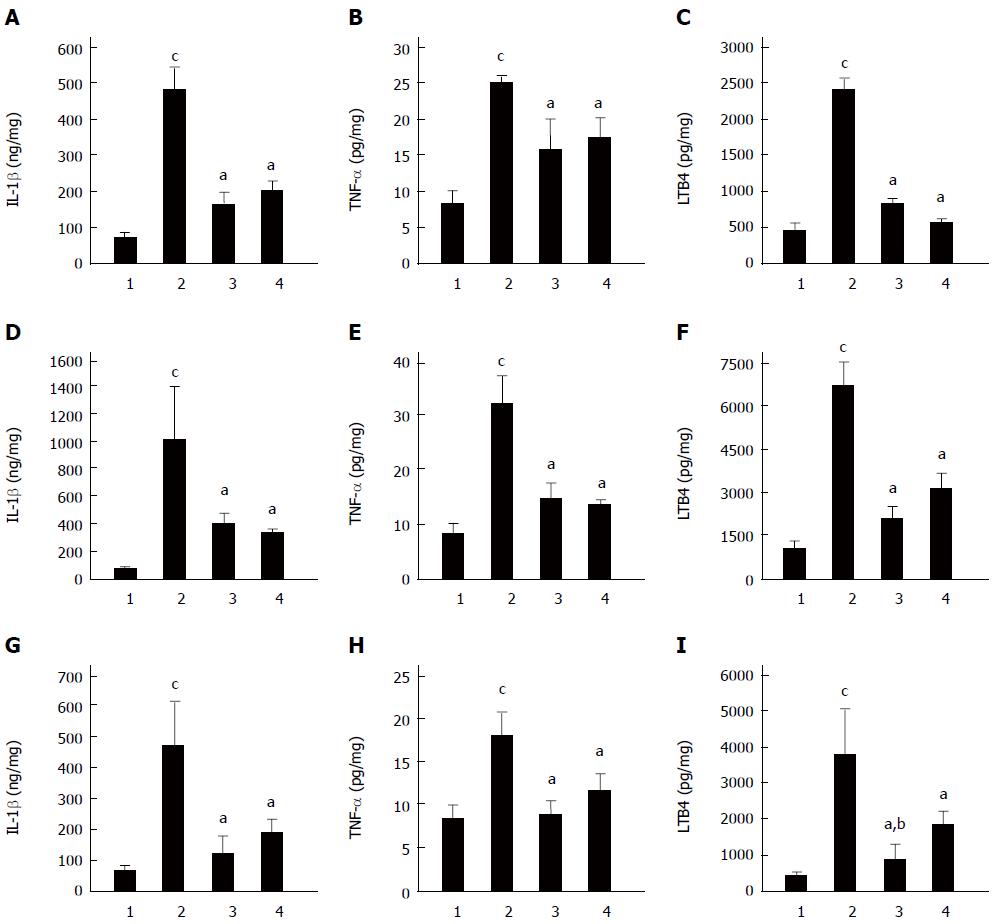
Figure 5 Effect of Clostridium butyricum on the levels of IL-1β, TNF-α and LTB4 in the gastric mucosa of mice with gastric ulcers induced by alcohol, cold stress or pylorus ligation.
Gastric ulcer models were induced by alcohol (A-C), cold stress (D-F) or pylorus ligation (G-I), respectively. The levels of IL-1β (A, D, G), TNF-α (B, E, H) and LTB4 (C, F, I) in gastric tissue of different GU mice were quantified. For each GU model, there were four different groups: Sham control group (1), Model group (without pretreatment) (2), Clostridium butyricum (C. butyricum) pretreatment group (3) and Omeprazole pretreatment group (4). The data were expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6). aP < 0.01 vs Model group; bP < 0.01 vs Omeprazole group; cP < 0.01 vs Sham control group.
-
Citation: Wang FY, Liu JM, Luo HH, Liu AH, Jiang Y. Potential protective effects of
Clostridium butyricum on experimental gastric ulcers in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(27): 8340-8351 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i27/8340.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8340